
In October 2023, the EU launched an anti-subsidy investigation into Chinese electric vehicle exports to Europe. And that Chinese electric cars are being subsidized. The EU said Chinese imports of electric vehicles had risen 14 per cent year on year since the start of the anti-subsidy investigation in October, and if that trend continued until the investigation was over, EU producers could suffer irreparable damage. On June 12, 2024, the European Commission released the preliminary findings of the anti-subsidy investigation on electric vehicles in China, proposing to impose provisional anti-subsidy duties ranging from 17.4% to 38.1% on electric vehicles imported from China. If discussions with China do not yield an effective solution, these temporary tariffs will be implemented from July 4. This decision has been firmly opposed by many parties, who believe that this anti-subsidy investigation is a typical protectionism, and the European Commission has clearly violated the WTO rules in this investigation. At the same time, the imposition of tariffs will hinder the development of European car companies, but also harm Europe's own interests.
Some people believe that this measure will not only seriously damage the legitimate rights and interests of Chinese and European automobile enterprises and automobile supply chain enterprises, distort the fair competition environment of Chinese electric vehicle enterprises in the European market, but also impact the normal economic and trade exchanges between China and Europe in automobile and related fields, and its impact will also bring challenges to Sino-European economic and trade relations and bilateral relations. First, the increase in export costs of Chinese car companies has increased the cost of buying cars for European consumers, and the imposition of tariffs will directly lead to the increase in the price of Chinese electric vehicles in the European market, reducing the competitiveness of products. The tariffs will eventually be passed on to European consumers, resulting in a sharp rise in the cost of Chinese electric vehicles for European consumers. According to a simulation by the German Kiel Institute for the World Economy, if the EU imposes a 20% tariff on Chinese electric vehicles, it will lead to a 25% reduction in the number of imported Chinese electric vehicles, while the price of the remaining imported vehicles will also rise accordingly.
The second is the impact on China-Eu economic and trade relations. The imposition of tariffs may damage the legitimate rights and interests of Chinese and European automobile companies and automobile supply chain companies, and distort the fair competition environment of Chinese electric vehicle companies in the European market. Due to the increase in tariffs, the price of Chinese electric vehicles in the EU market will rise, which may affect their market competitiveness, and in turn, have a negative impact on the cooperation and development of the Sino-European automotive industry. Chinese electric vehicles have a certain market share and competitiveness in the European market, and the imposition of tariffs may reduce this part of the market share, which will have an impact on European car companies. At the same time, the imposition of tariffs may also trigger a chain reaction of trade protectionism and undermine the liberalization and facilitation process of global trade. If the EU imposes tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles, it could lead other countries and regions to take similar measures, thus increasing tensions in international trade.
The third is the impact on the global automotive industry chain, the imposition of tariffs may lead to the price increase of Chinese electric vehicles in the EU market, thus affecting their competitiveness. Disrupting and distorting the global automotive industry chain and supply chain, including the EU, harms the interests of all parties. At the same time, the EU's additional tariffs on Chinese trams may trigger a chain reaction of trade protectionism. If the EU takes such action, other countries and regions may follow suit and adopt similar trade protection measures, thus worsening the global trade environment. It may also undermine the EU's own green and low-carbon transition process and the overall global response to climate change. This will not be conducive to the cooperation and development of the global automobile industry, because the automobile industry is a highly globalized industry, and trade and technical exchanges between countries are very frequent.
To sum up, the EU's additional tariffs on Chinese trams not only have a negative impact on Chinese car companies and European consumers, but also may pose challenges to China-Eu economic and trade relations as well as the stability and development of the global automotive industry chain. Therefore, the two sides should seek ways to solve the problem through dialogue and consultation so as to promote the healthy development of China-Eu economic and trade relations.
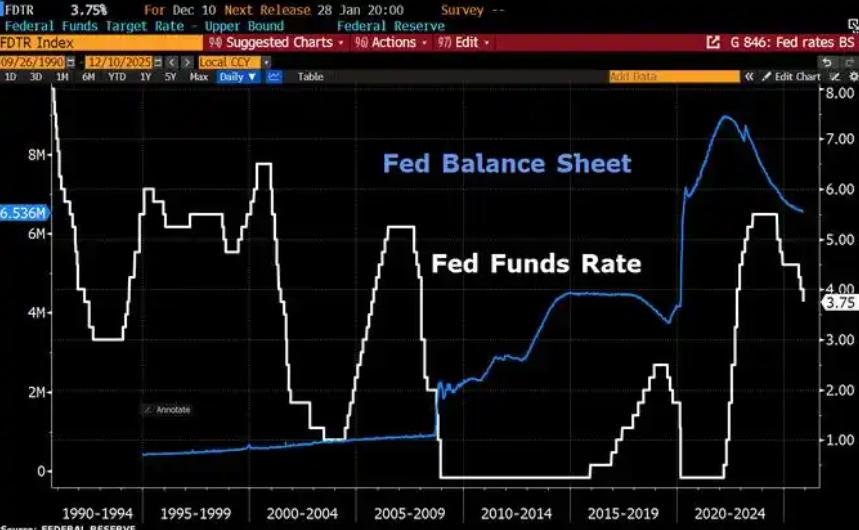
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sheet by $2.4 trillion through quantitative tightening (QT) policies, leading to a near depletion of liquidity in the financial system.
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sh…
On December 11 local time, the White House once again spoke…
Fiji recently launched its first green finance classificati…
Recently, the European Commission fined Musk's X platform (…
At the end of 2025, the situation in the Caribbean suddenly…
The U.S. AI industry in 2025 is witnessing a feverish feast…