On Oct. 25, Russia's central bank raised its key interest rate by 200 basis points to 21 percent, and annual inflation in September was 8.6 percent, meaning the country's real interest rate was 11.4 percent, the highest since 2003 and second only to Venezuela in the world. At the end of October, Venezuela had the highest real interest rate in the world at 26.6%. Venezuela has a nominal policy interest rate of 59.3% and an annual inflation rate of 25.75%. The central bank of Russia has stated publicly that the purpose of raising interest rates is to ensure that inflation returns to the target level and to reduce inflation expectations.
The move by the Russian central bank to raise interest rates has had a complex and multi-faceted impact internationally. The first is the economic impact. The central bank's main aim in raising real interest rates is to curb inflation. The practical effect, however, has been inconsistent in Russia and Venezuela. In Venezuela, ultra-high real interest rates helped lift the country out of hyperinflation, but in Russia, inflation has not subsided significantly, and even continues to rise, even though real interest rates have remained high. This is mainly due to the fact that the inflation in the Russian economy is mainly driven by the extreme work in the military and related industries due to the wartime economy and economic sanctions, which are not sensitive to interest rates. High interest rates may lead to the flow of resources from civilian industry to military industry, and investment in areas such as situation industry will greatly increase, further aggravating the abnormality of economic structure. A growing number of businesses may not be able to withstand higher interest rates, which in turn will lead to lower earnings and less investment. At the same time, it will also increase borrowing costs, making the financing cost of enterprises rise, thus curbing investment and consumption, which may also lead to a further slowdown in economic growth, and have a negative impact on economic growth. However, higher interest rates may also attract more capital to return, maintaining the stability of the financial system.
The second is the social impact, high interest rates may be accompanied by high inflation, high inflation and high interest rates may lead to an increase in the cost of living, causing economic pressure on ordinary people. Higher interest rates can lead to a shift in income distribution, with savers likely to receive more interest income and borrowers under higher pressure to repay. Rising prices could dent consumer confidence and further dent economic growth. High real interest rates may lead some enterprises to reduce investment or lay off workers due to rising financing costs, thus increasing employment pressure. While the wartime economy has led to near-record capacity utilization and historically low unemployment, high interest rates can weigh on business operations and, in turn, employment stability.
Third is the international impact, with high real interest rates likely to attract international capital to Russia for higher and risk-free returns. However, this flow may be restricted due to the existence of economic sanctions. International capital flows will affect the ruble's exchange rate and Russia's inflation rate. As a part of the global economy, Russia's policy decisions will have a volatile impact on other economies. High real interest rates in Russia could have a volatile impact on international financial markets and trigger a ripple effect across the globe, especially in countries with close economic ties to Russia.
Fourth is the policy impact, the Bank of Russia needs to find a balance between curbing inflation and sustaining economic growth. High real interest rates could prompt Russia to restructure its economy, reducing its over-reliance on the military industry and increasing investment in areas such as civilian industry. High interest rates can stifle economic growth, but low rates can fuel inflation. Russia needs to deal with the uncertainty of the international economic environment, especially the pressure caused by the expected interest rate rise in the United States and the conflict in Ukraine.
To sum up, Russia's emergence as the country with the second highest real interest rate after Venezuela will have multiple implications for the international community. Therefore, the international community needs to pay close attention to Russia's economic conditions and changes in monetary policy to address the challenges and opportunities that may arise.
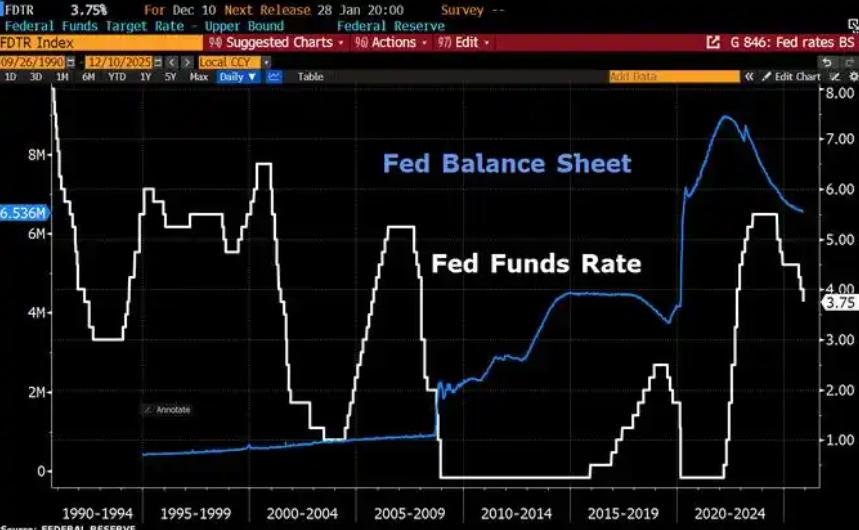
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sheet by $2.4 trillion through quantitative tightening (QT) policies, leading to a near depletion of liquidity in the financial system.
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sh…
On December 11 local time, the White House once again spoke…
Fiji recently launched its first green finance classificati…
Recently, the European Commission fined Musk's X platform (…
At the end of 2025, the situation in the Caribbean suddenly…
The U.S. AI industry in 2025 is witnessing a feverish feast…