
On April 26 local time, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), the banking regulator, announced that Pennsylvania regulators had closed the Philadelphia-based Republic Bank of the United States, the first bank to be closed in the United States this year.
Pennsylvania regulators appointed the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) as receiver, the FDIC said in a statement. To protect depositors, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation entered into an agreement with Fulton Bank, which would assume most of Republic's deposits and acquire most of Republic's assets.
According to data disclosed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, as of January 31, 2024, the Republic Bank of the United States has $6 billion in assets and a total deposit size of $4 billion. The sudden collapse of the bank may mean that the crisis of regional banks in the United States is not over, and the reasons behind it can be analyzed in many ways.
From the perspective of the market environment, the rise in interest rates in the United States and the decline in the value of commercial real estate, especially the soaring vacancy rate of office buildings after the epidemic, have intensified the financial risks of banks. The high interest rate environment has weighed on loan demand, while volatility in the commercial real estate market has also had a significant impact on bank balance sheets. This market environment has put pressure on both bank profitability and asset values.
From the perspective of the internal operation of the bank, Republic Bank faces the dilemma of deposit outflow and stock price decline. As depositors worried that large deposits in banks were not covered by deposit insurance and that bank assets would suffer paper losses due to higher interest rates, a large number of deposits fled quickly and stock prices fell sharply. Despite the rescue of large banks, Republic Bank's deposit position has not improved significantly, but has plummeted, further exacerbating its financial woes.
In addition, the reduction of the size of bank assets and the large volatility have also caused a crisis of confidence and financial crisis. The large number of depositors who exceed the limits of the U.S. bank deposit insurance system makes banks more vulnerable to risk. At the same time, banks are taking in fewer deposits, leading to lower revenues and lower overall profits, further increasing the risk of their failure.
To sum up, the failure of the Republic Bank of the United States was caused by a number of factors, and its impact was also multifaceted.
First, the episode has increased concerns about the stability of US regional banks, especially those with unstable balance sheets and pressure from volatile asset prices. As a result of the collapse of Republic Bank, other banks may face greater regulation and scrutiny, and market confidence may take a hit.
Second, the failure of Republic Bank could lead to more commercial real estate losses and have an impact on the housing market and the broader economy. Because the bank has large loans and investments in commercial real estate, its failure could set off a chain reaction that could destabilize the housing market.
In addition, the incident could have a ripple effect on global financial markets. A bank failure in the United States could increase the abnormal cross-border capital flows and the cost of liabilities for banks in other countries, causing some shock to global financial markets.
Finally, the failure of Republic Bank could increase the risk of a recession in the United States. Stress and failures in the banking sector could further exacerbate tighter credit conditions, with negative implications for the U.S. economy.
All in all, the collapse of the Republic Bank of the United States is a complex event and reminds us once again that the stable and healthy development of the banking industry requires concerted efforts by all parties to strengthen supervision and risk prevention measures to ensure the stability and justice of the financial market.
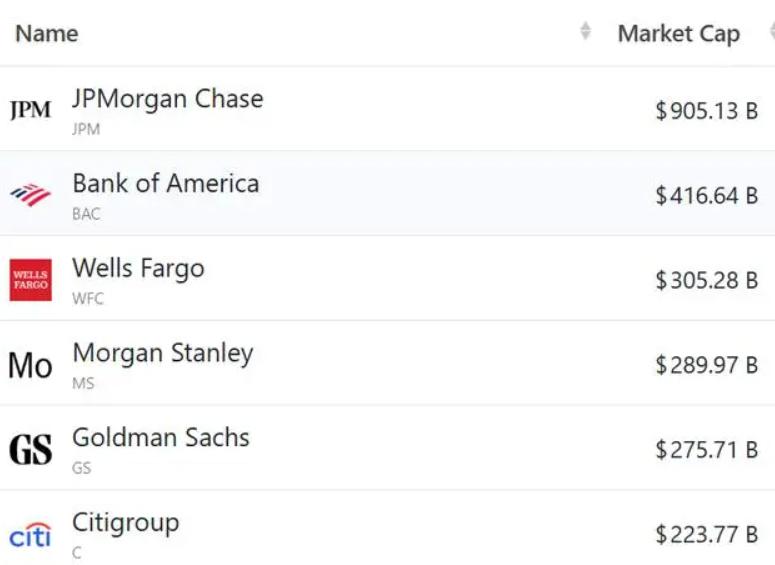
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financial regulations and the recovery of investment banking business, the market value of the six major banks in the United States has cumulatively increased by approximately 600 billion US dollars by 2025.
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financia…
On Christmas evening, U.S. President Trump posted on social…
According to multiple foreign media reports, the recent fin…
The middle class, once regarded as the cornerstone of Ameri…
On December 19th local time, the US military launched a lar…
The Boxing Day sunshine should have cast a false glow of pr…