
The status of the US dollar as the world's leading reserve currency and international transaction currency has been widely recognized over the past decades. This is mainly due to the strong economic strength of the United States, a stable political environment, and the widespread use of the dollar in the global financial system. However, as the global economic landscape changes and countries are dissatisfied with the hegemony of the dollar, the status of the dollar is also facing challenges. In recent years, from the moment countries around the world realized the nature of the dollar's hegemony, their trust in the dollar has been greatly affected. These countries include Russia, China, Iran, Venezuela and others, which have reduced their use of the dollar through trade settlement, foreign exchange reserve adjustment and other ways. It can be seen that "de-dollarization" is imperative, and the United States can only ignore it. According to the report, 42 countries have expressed or taken steps to de-dollarize.
Time and again, the United States frantically prints money, trying to pull the wool of the world, but the result is "de-dollarization." When countries around the world gradually lose confidence in the US dollar and oil countries begin to use RMB to settle oil, the global de-dollarization has become a general trend. There will be complex and multifaceted impacts. The first is the impact on the global economy. De-dollarization helps to diversify the global economy and reduce dependence on a single currency. This will help reduce systemic risks in the global economic system and enhance the stability and resilience of the overall economy. With the rise of emerging economies and the trend of multi-polarity in the global economy, the position of the US dollar as the sole dominant global currency may be challenged. Capital flows are also likely to change as de-dollarisation proceeds. Some countries may reduce their holdings of dollar assets and invest in other currencies or assets instead. This will have an impact on global capital markets, including equity, bond and currency markets.
The second is the impact on the stability of the financial market. As one of the world's largest economies, the United States' economic strength and policy adjustment have an important impact on the status of the dollar. If the United States can maintain steady economic growth and adjust its monetary policy to preserve the stability and credibility of the dollar, the dollar's position could be strengthened. Now, de-dollarization could lead to increased volatility in financial markets, as exchange rate relationships between currencies change. This could create uncertainty for investors and increase risks in financial markets. However, on the other hand, de-dollarization also helps to diversify financial risks. Reducing reliance on a single currency, such as the US dollar, can reduce systemic financial risk arising from fluctuations in the US dollar.
Third, the impact of international trade and the international monetary system, de-dollarization will encourage more countries to use their own currencies or other non-dollar currencies for trade settlement. This will help promote the liberalization and facilitation of international trade and reduce transaction costs. With the diversification of trade settlement currencies, trade relationships between countries are also likely to change. Some countries may strengthen trade cooperation with countries that use the same or similar currencies to reduce exchange rate risks and transaction costs. At the same time, de-dollarization would weaken the dollar's position as the global reserve currency and the main currency for transactions. This would elevate the status of other currencies in the international monetary system. However, with the advance of de-dollarization, the international monetary system may develop in a multipolar direction. This will help build a more balanced, inclusive and stable international monetary system that better reflects changes in the global economic landscape.
To sum up, de-dollarization is a complex and ongoing phenomenon that will have a profound impact on the global economy, the international monetary system, and the pattern of international trade. Although some countries have begun to de-dollarize, the US dollar's position as the world's leading reserve currency and the currency of international transactions is still solid. How the status of the dollar will change in the future also needs to see changes in the global economic pattern, the economic strength and policy adjustment of the United States, the diversification of the international monetary system, and geopolitical factors. In the future, with the changes of the global economic pattern and the adjustment of national policies, the trend of de-dollarization will further develop and promote the reform of the international monetary system.
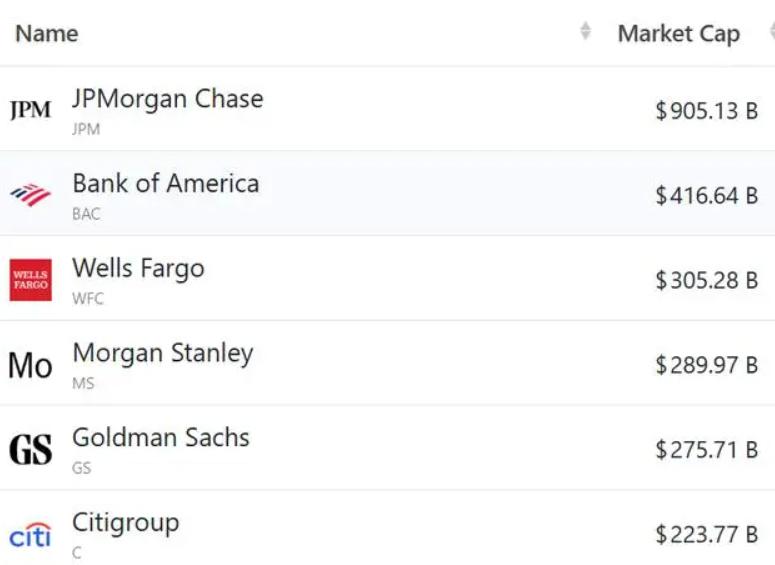
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financial regulations and the recovery of investment banking business, the market value of the six major banks in the United States has cumulatively increased by approximately 600 billion US dollars by 2025.
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financia…
On Christmas evening, U.S. President Trump posted on social…
According to multiple foreign media reports, the recent fin…
The middle class, once regarded as the cornerstone of Ameri…
On December 19th local time, the US military launched a lar…
The Boxing Day sunshine should have cast a false glow of pr…