
Recently, Federal Reserve Chairman Powell stated at a congressional hearing that the Federal Reserve does not need to wait for inflation to fall below 2% before considering interest rate cuts. If the wait is too long, inflation may be too low, far below 2%, which is not what the Federal Reserve hopes to see. Powell's statement reflects the Federal Reserve's optimistic expectations for the future trend of inflation, which is expected to gradually decline to a more moderate level.
In addition to inflation, the Federal Reserve also closely monitors economic growth and employment conditions. While inflation is slowing down, if economic growth remains stable and the job market is strong, the Federal Reserve may consider adjusting monetary policy at an appropriate time to support sustained and healthy economic development.
After Powell's statement, financial markets usually show positive reactions. Asset prices such as the stock market and bond market may rise, reflecting investors' optimistic attitude towards the future economic outlook. However, although this statement has boosted market confidence to some extent, it may also bring some adverse effects.
One is the increase in inflation expectations. If the market generally expects the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates early, this may raise concerns about inflation in the market. Lowering interest rates is often seen as a signal of monetary easing, which may lead to more money supply entering the economic system, thereby pushing up price levels. If inflation expectations rise too quickly, it may weaken consumer confidence and affect consumption and investment decisions.
The second is to cause fluctuations in the financial market. Although the market may respond positively to expectations of interest rate cuts in the short term, in the long run, financial markets may experience fluctuations due to policy uncertainty. Investors need to constantly adjust their investment portfolios to cope with policy changes, which may lead to unnecessary market fluctuations. In addition, if the Federal Reserve's interest rate cut action does not match market expectations, it may also trigger significant market fluctuations.
Thirdly, it may increase the debt burden. Lowering interest rates usually leads to a decrease in borrowing costs, thereby encouraging businesses and individuals to increase borrowing. However, if the scale of borrowing is too large, it may lead to an increase in debt burden, especially in cases of economic slowdown or recession. This may have a negative impact on the profitability and solvency of the enterprise, which in turn affects the stability of the entire economic system.
The fourth is to cause capital outflow. Lowering interest rates may lead to capital outflows from the United States, as other countries may offer higher interest rate returns. This may lead to a decline in the US dollar exchange rate, which in turn will have an impact on US exports and the global economy. In addition, the instability of capital flows may also increase the risk of financial markets.
The effectiveness of monetary policy may be questioned. If the Federal Reserve cuts interest rates too early or too much, it may raise doubts in the market about the effectiveness of monetary policy. This may weaken the credibility and influence of the Federal Reserve in the financial markets, thereby affecting the effectiveness of its future policy implementation.
Finding a balance between inflation and economic growth is an important challenge currently facing the Federal Reserve. If interest rate cuts lead to rapid inflation and economic growth fails to keep pace, it may trigger stagflation risks. This will make the Federal Reserve face greater difficulties in controlling inflation and stimulating economic growth.
As one of the major economies in the world, the monetary policy adjustment of the United States has a significant impact on the global economy. The early rate cut by the Federal Reserve may trigger monetary policy adjustments in other countries and regions, which could have a chain reaction on global financial markets. Therefore, the Federal Reserve needs to carefully weigh various factors when formulating monetary policy to ensure its effectiveness and sustainability. At the same time, market participants also need to closely monitor changes in economic data and the policy trends of the Federal Reserve in order to make wiser investment decisions.
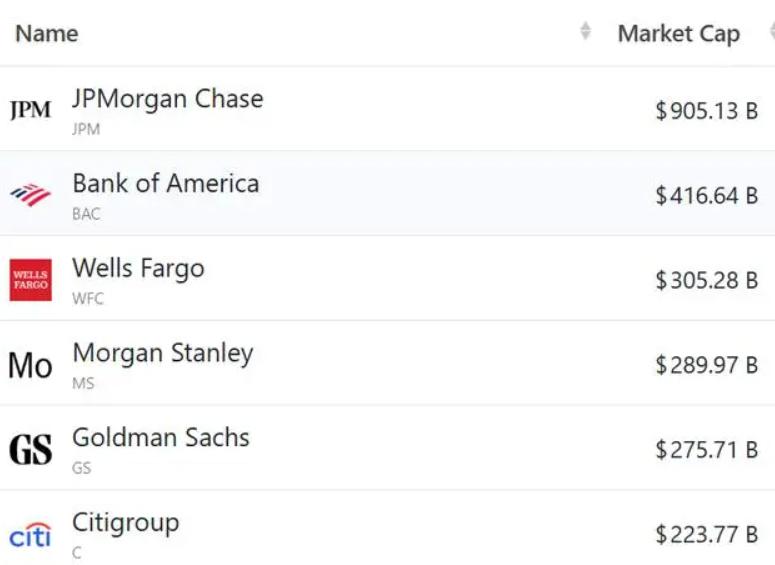
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financial regulations and the recovery of investment banking business, the market value of the six major banks in the United States has cumulatively increased by approximately 600 billion US dollars by 2025.
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financia…
On Christmas evening, U.S. President Trump posted on social…
According to multiple foreign media reports, the recent fin…
The middle class, once regarded as the cornerstone of Ameri…
On December 19th local time, the US military launched a lar…
The Boxing Day sunshine should have cast a false glow of pr…