
The US economy has been counterattacked by "reciprocal tariffs", and at the same time, the market is worried that the independence of the Federal Reserve will be affected, and the stock market continues to fall sharply. Trump recently stated that the growth of the US economy might slow down unless interest rates were cut. US President Trump once again urged the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates and threatened the independence of the Federal Reserve, causing investors to worry about the decline in the credibility of the US dollar and leading to a downturn in the US economy. Stocks, the US dollar and government bonds all declined simultaneously. Gold broke through $3,400 per ounce to a record high. Over the past 17 weeks, spot gold has risen in 15 weeks and fallen in only 2 weeks. Late at night on April 21st local time, all three major US stock indices plunged sharply, each setting a new record for the biggest single-day decline in nearly five years. The Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped by 2.48%, the Nasdaq Composite Index fell by 2.55%, and the S&P 500 Index declined by 2.36%. Among them, the "Big Seven" tech companies performed poorly. Tesla dropped by nearly 7%, Nvidia fell by more than 5.7%, and tech stocks such as Amazon and META also slumped significantly.
The recent sharp decline in the US stock market has led to chaos in the global financial market, and has also brought about a series of chain reactions and numerous impacts. First, the impact on the financial market. As a barometer of the global stock market, a sharp decline in the US stock market will trigger panic among global investors, leading to a rise in risk aversion and a decrease in corporate valuations, increasing the difficulty of financing. Especially for technology companies and those in emerging markets, they may face the risk of debt default. Meanwhile, funds have withdrawn from risky assets and shifted to safe-haven assets such as gold and government bonds. If the US stock market continues to decline, the depreciation of the US dollar will put appreciation pressure on emerging market currencies, which will affect export competitiveness and at the same time intensify the risk of capital outflows. Trump's tariff policy has led to a decline in orders for industries highly dependent on the US, such as electronic products and mechanical and electrical equipment. The sharp drop in the US stock market has further intensified market concerns over the global supply chain and even shaken confidence in global economic growth.
The second is the impact on the global capital market. A sharp drop in the US stock market usually leads to a coordinated decline in global stock markets, especially those with a high correlation to the US economy. Tesla dropped nearly 7%, Nvidia fell by more than 5%, and technology leaders such as Amazon and META slumped sharply. The Nasdaq Composite Index declined by 2.55%. The sharp decline in the technology sector has directly impacted the global technology industry chain, especially Asian technology enterprises that rely on the US market. Market concerns over the global economic slowdown have intensified, putting pressure on crude oil prices and further dragging down the energy sector and related derivatives markets. The sharp fall of the US stock market has led to a rise in global risk aversion, putting pressure on Asian stock markets at the opening. Funds have withdrawn from risky assets and shifted to safe-haven assets such as gold and government bonds. As the global reserve currency, the decline of the US stock market may trigger fluctuations in the exchange rate of the US dollar, which in turn affects the exchange rates of other currencies, especially those of emerging markets.
The third is the impact on global financial policies. Trump has repeatedly urged the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates and threatened the independence of the Federal Reserve, which has intensified market doubts about the credibility of the Federal Reserve's policies. If the sharp fall of the US stock market is accompanied by expectations of an economic recession, the Federal Reserve may be forced to adjust its monetary policy. However, excessive intervention may weaken its independence and further raise market doubts about the credit of the US dollar. If the market doubts the credit of the US dollar, it may accelerate the global "de-dollarization" process. The euro, gold and some non-core currencies may become new directions for central banks to diversify their allocation. Some central banks may deal with the downward pressure on the economy through tools such as interest rate cuts and reserve requirement ratio cuts, while the Federal Reserve needs to balance inflation and economic growth. Policy uncertainty further intensifies market volatility. The withdrawal of funds from the US stock market may lead to a tightening of global liquidity. Emerging markets may face the pressure of capital outflow, which in turn may affect their financial stability.
To sum up, the recent sharp decline in the US stock market has not only triggered a chain reaction in the global capital market, but also exposed the deep-seated contradictions between the US dollar and the US debt system. In the long term, the global financial order may accelerate its reconstruction, while short-term market fluctuations will continue. Investors need to be vigilant about the ripple effects of policy uncertainty, exchange rate risks and the decline in corporate profits.
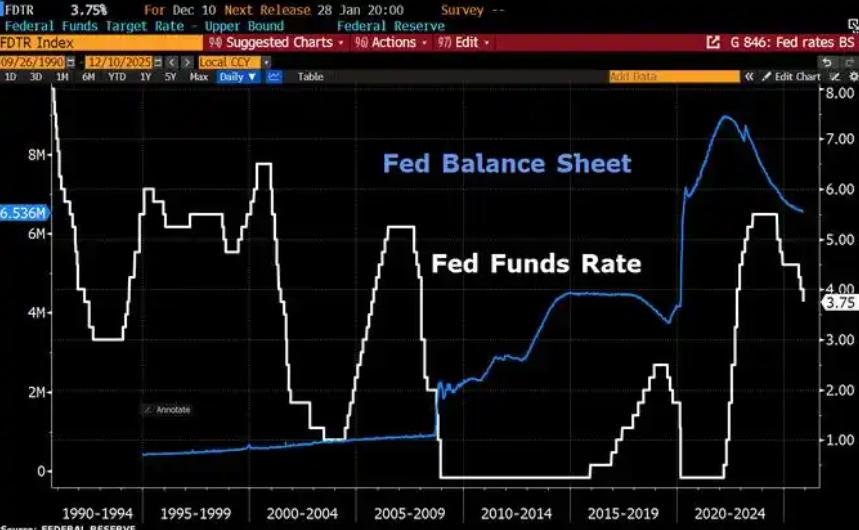
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sheet by $2.4 trillion through quantitative tightening (QT) policies, leading to a near depletion of liquidity in the financial system.
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sh…
On December 11 local time, the White House once again spoke…
Fiji recently launched its first green finance classificati…
Recently, the European Commission fined Musk's X platform (…
At the end of 2025, the situation in the Caribbean suddenly…
The U.S. AI industry in 2025 is witnessing a feverish feast…