
In April 2025, the global trade landscape was thrown into turmoil due to the extensive tariff policies announced by US President Donald Trump. Against this backdrop, the European Union is actively preparing countermeasures against the US, aiming to safeguard its economic interests while preventing a full-scale escalation of trade conflicts. These measures not only concern the future direction of EU-US economic and trade relations but also have a profound impact on the global trade order.
I. Background and Content of Countermeasures
Since early April, the Trump administration has imposed universal tariffs on imports from almost all trading partners, including a 20% "reciprocal tariff" on EU goods and a threat of an additional 25% tariff on key sectors such as automobiles. This move has directly impacted the EU's export economy. According to 2024 data, the EU's total exports to the US amounted to 532 billion euros, with automobiles, steel, and aluminum products already facing a 25% tariff barrier. To counter this pressure, the European Commission plans to launch the first round of countermeasures on April 15, with a proposed tariff on $28 billion worth of US goods, including meat, grains, wine, wood, clothing, and daily necessities.
II. Internal Disagreements and Coordination Challenges within the EU
There are significant differences within the EU regarding countermeasures. France advocates a tough stance and even suggests that European companies suspend investment in the US until the situation clarifies. Ireland, on the other hand, calls for a "thoughtful and measured" response, as one-third of its exports rely on the US market. Italy questions the necessity of countermeasures, fearing an escalation of trade tensions. Additionally, the EU's proposal to impose a 50% tariff on bourbon whiskey has sparked internal disputes, with France and Italy worried about damage to their wine industries, while Trump threatens a 200% retaliatory tariff on EU alcoholic beverages.
To bridge these differences, the EU plans to implement countermeasures in two phases: the first set of tariffs will take effect on April 15, with the rest to be implemented one month later. Despite internal disagreements, EU member states generally agree that countermeasures should balance "firmness" with "restraint" to avoid a full-scale trade war.
III. Economic and Political Considerations of Countermeasures
The economic logic behind the EU's countermeasures lies in using reciprocal tariffs to force the United States to renegotiate trade terms. However, this strategy faces multiple challenges. On the one hand, the EU's trade surplus with the United States is mainly concentrated in the service sector, while the United States holds an advantage in goods trade. A tariff war could have a greater impact on the EU's manufacturing industry. On the other hand, the EU is highly dependent on exports to the United States, especially in the automotive and agricultural sectors. Countermeasures could trigger retaliatory tariff hikes from the United States, further damaging the EU's economy.
Politically, the EU must balance its relationship with the United States and internal unity. Countries like Germany emphasize the necessity of countermeasures but are concerned that a trade war could harm the interests of European businesses. France, on the other hand, attempts to use countermeasures to pressure the United States and gain more support on issues such as the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Additionally, there are differences within the EU regarding the decision-making mechanism for countermeasures. Some member states are concerned about the applicability of the "Anti-Coercion Instrument Bill" and worry that over-reliance on tariff measures could weaken the EU's influence in global trade rule-making.
IV. Potential Impacts and Future Prospects of Countermeasures
If the EU's countermeasures are implemented, they may trigger three major chain reactions: First, the global supply chain is at risk of restructuring, especially in industries such as automobiles and electronics that are highly dependent on the US and European markets. Second, the escalation of trade frictions between the US and the EU may accelerate the trend of "de-globalization" and promote the deepening of regional trade agreements such as RCEP. Third, the EU may need to reevaluate its strategy towards the US and possibly strengthen cooperation with China to balance the pressure from the US.
However, the long-term effects of the countermeasures remain uncertain. If the US and the EU fail to reach a compromise through negotiations, the tariff war may continue to escalate, leading to a sharp increase in economic costs for both sides. The EU needs to find a balance between safeguarding its own interests and avoiding a trade war, while promoting the reform of the multilateral trade system to address the challenges of unilateralism.
The EU's countermeasures are not only an emergency response to Trump's tariff policies but also a strategic game to reshape the economic and trade relations between the US and the EU. In the future, the EU needs to seek breakthroughs in internal unity, economic resilience, and global rule-making to maintain its interests in a complex and volatile international environment.
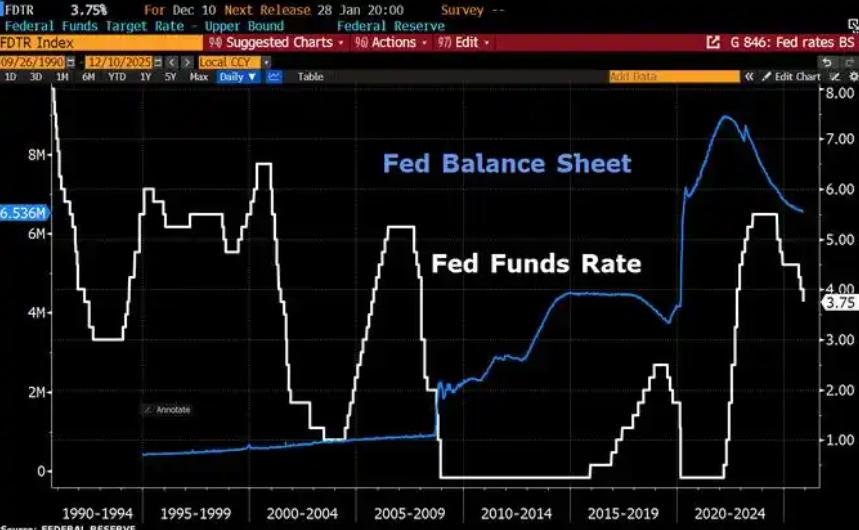
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sheet by $2.4 trillion through quantitative tightening (QT) policies, leading to a near depletion of liquidity in the financial system.
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sh…
On December 11 local time, the White House once again spoke…
Fiji recently launched its first green finance classificati…
Recently, the European Commission fined Musk's X platform (…
At the end of 2025, the situation in the Caribbean suddenly…
The U.S. AI industry in 2025 is witnessing a feverish feast…