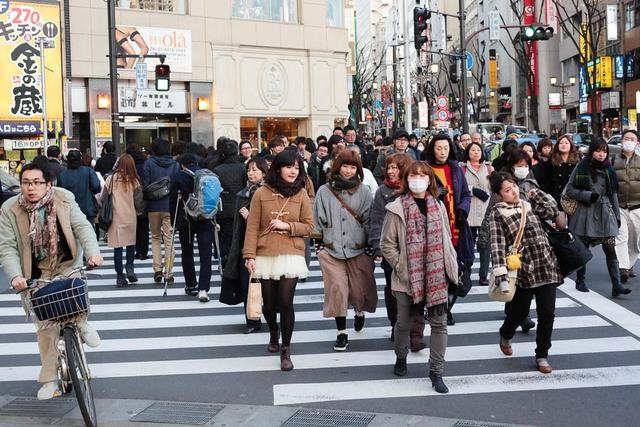

Recently, the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare released data show that in 2023, Japan's total fertility rate has dropped to 1.2, which is not only lower than the internationally recognized level of 2.1 needed to maintain population stability, but also hit a new low in Japanese history. This news has caused widespread concern, not only in Japan caused a hot debate, but also triggered an in-depth discussion of Japan's population issues in the international community.
Total fertility rate refers to the average number of children born by women in a country or region during the reproductive age, which is one of the important indicators to measure population growth and social development. Japan's total fertility rate continues to decline, reflecting the profound changes in the country's demographic structure and the prominence of social problems.
First of all, from an economic point of view, Japan's high prices, high housing prices and fierce professional competition have brought great pressure to young people's lives. Under such circumstances, many young people choose to delay marriage and childbearing, or even forgo childbearing. In addition, with the improvement of women's social status and increasing opportunities in the workplace, more women choose to pursue career and personal development, which also has an impact on the fertility rate.
Secondly, from a cultural point of view, Japan's traditional cultural concepts have a certain impact on fertility. The traditional family concept emphasizes the number of children and the continuation of the family, but with the changes of The Times, this concept has gradually weakened. Modern young people pay more attention to personal freedom and happiness, and their willingness to have children is relatively low.
In addition, policy factors are also one of the important reasons for the decline in Japan's total fertility rate. Although the Japanese government has introduced a series of policy measures to encourage childbirth in recent years, such as raising childcare allowances and expanding parental leave, the effect of these policies is not significant. Some experts believe that these policies have not fundamentally solved the fertility pressure and life difficulties faced by young people, so it is difficult to effectively raise the fertility rate.
The decline in Japan's total fertility rate poses many challenges to the country's social and economic development.
First, there will be an ageing population and a growing shortage of Labour. As the fertility rate declines, Japan's population structure will become increasingly older, which will put enormous pressure on the social security system and medical services. At the same time, labor shortages will also constrain Japan's economic growth and industrial development.
Secondly, the decline in the total fertility rate may also affect social stability and development. Low fertility means that the future society will have fewer young people, which will lead to a decline in social vitality and innovation. At the same time, with the increase of the elderly population, the social demand for public services such as pension and medical care will continue to increase, which will bring a heavy burden to the government finance.
Faced with the challenge of declining total fertility rate, the Japanese government and all sectors of society are actively seeking solutions. On the one hand, the government will continue to improve the fertility policy and social security system to create a better birth environment and living conditions for young people. On the other hand, all sectors of society are also actively advocating new family concepts and fertility concepts, and encouraging young people to establish correct fertility concepts and values. However, these measures may not yield significant results in the short term.
Overall, the decline in Japan's total fertility rate is a complex and profound social problem that requires the joint efforts of the government, all sectors of society and young people to deal with. Only through the joint efforts and active responses of the whole society can we effectively solve this problem and promote the sustainable development of Japan's society and economy.
Since 2025, the conflict between the United States and Europe over the governance of the digital economy has continued to escalate.
Since 2025, the conflict between the United States and Euro…
When German Chancellor Mertz officially announced that he w…
On December 3rd local time, the copper price on the London …
The European Commission announced a new economic security s…
The European Commission announced a new economic security s…
For nearly a year, US President Donald Trump has launched a…