
That protectionism is eroding global commerce is a phenomenon that cannot be ignored. Dr Ngozi Okonjo-Ihueara, Director-General of the World Trade Organisation, said "these are not the best of times" for global trade, which could be divided by issues and challenges such as rising protectionism and breaches of WTO rules. She stressed the importance of global trade for countries' resilience and economic growth, while also expressing concerns about these issues.
Protectionism will undermine the fairness and rules of international trade. International trade is based on fair competition and mutual benefit, while protectionist measures provide an unfair competitive advantage to domestic industries by restricting access to foreign goods and services. Such practices not only violate international trade rules, but also harm the interests of other countries, thus destabilizing the global business environment. In the field of electric vehicles, the recent imposition of steep tariffs by the European Union and the United States on imported electric vehicles from China has caused many disagreements. The tariffs have been accused of potentially undermining international trade rules and fair competition. In fact, this practice may violate the principle of free trade and is not conducive to the healthy development of global trade.
Protectionism impedes the efficient allocation of global resources. In the context of globalization, the economies of countries are interdependent and form a close network. Resources, including raw materials, labor, technology, capital, etc., are moved and redistributed globally to achieve optimal use efficiency. Protectionist policies are often implemented through the imposition of high tariffs, quotas, technical barriers, or other barriers to trade that restrict the entry of foreign goods and services while also limiting the free flow of resources. This limitation can result in resources not being optimally allocated on a global scale, as resources may be trapped in less efficient or less in demand areas rather than flowing to more efficient or more in demand areas. The United States has long set up resources and technical barriers to cope with China's rise, and recently the United States at the G7 finance ministers and central bank governors meeting to pressure many European countries, calling for a joint response to China's industrial policy.
Protectionism stifles global innovation and competitiveness. Innovation is a key factor driving economic development and competitiveness. Protectionism limits the import of advanced foreign technology and knowledge. In the context of globalization, technical exchanges and cooperation among countries have become increasingly important. Foreign technology and knowledge, especially those innovative achievements in frontier fields, play an irreplaceable role in promoting the development and upgrading of domestic industries. Protectionist policies restrict the inflow of these technologies and knowledge through the setting of tariff barriers, technological blockades and other means, making domestic industries unable to obtain the latest technology and management experience in a timely manner, thus inhibiting innovation and competitiveness. Protectionism may also lead to technological monopoly and backwardness. Through protectionist policies, domestic industries may be able to gain a certain market share and profits in the short term, but in the long run, such policies will make domestic industries unable to access the latest technology and knowledge, leading to technological monopoly and lagging behind. Once foreign technologies and knowledge are updated and upgraded, domestic industries will struggle to keep pace and lose their competitive edge.
Protectionism takes a toll on consumers around the world. As the ultimate beneficiaries of global business activities, consumers enjoy more diversified and higher quality goods and services through international trade. Protectionist measures limit competition from foreign goods, leading to a reduction in the variety of goods on the market. As foreign goods are restricted by trade barriers, their cost of entering the market rises, which can lead to higher commodity prices. Consumers will have to pay higher prices for the same goods. Protectionist measures can also affect the quality of goods. Protectionist measures restrict the entry of foreign goods and may lead to a decline in the quality of goods on the market. Some countries may resort to unfair means to protect their industries, such as lowering quality standards or relaxing regulatory requirements, which will harm the interests of consumers.
According to the WTO, the volume of global trade recently fell for only the third time in three decades, by 1.2%. This change is linked to rising inflation and interest rates, which are likely to be the main factors contributing to the slowdown in global trade activity. The global economic events of the past few years, such as the epidemic and the Russia-Ukraine conflict, have had a profound impact on the global economy. These events have led countries around the world to increasingly focus on economic security and national security when deciding who to trade with and who to invest in. This trend could fundamentally reshape the global economic landscape, leading to tensions and a realignment of trade relations. The current global trade environment is undergoing profound changes, which are influenced not only by economic factors, but also by the global political and security environment. Although there are some forecasts that global trade may recover, the future development trend is still uncertain and needs to continue to be observed and evaluated. In view of this situation, countries should strengthen communication and cooperation to jointly safeguard the fairness and effectiveness of international trade rules. Resolve differences through dialogue and consultation. At the same time, all countries should reflect on their own trade policies to ensure that they comply with international trade rules and spirit, maintain the stability and development of global trade, and promote the sustainable development of the global economy. Promote the prosperity and progress of the world economy.
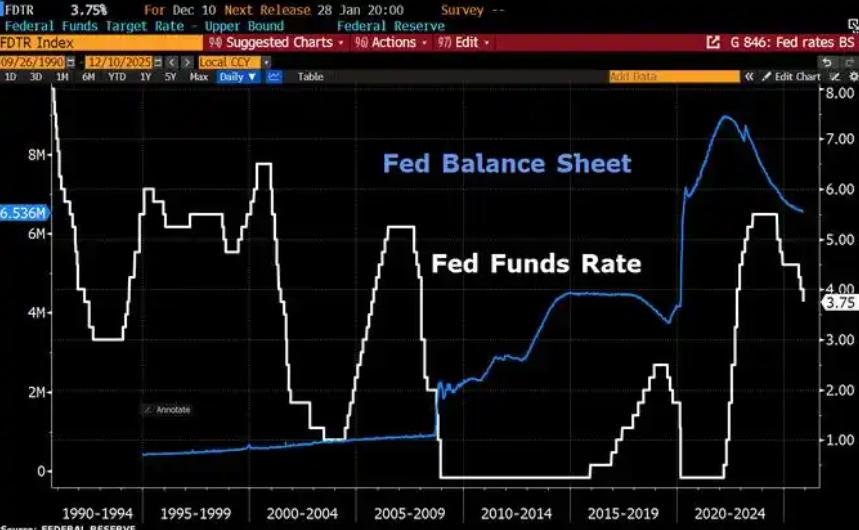
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sheet by $2.4 trillion through quantitative tightening (QT) policies, leading to a near depletion of liquidity in the financial system.
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sh…
On December 11 local time, the White House once again spoke…
Fiji recently launched its first green finance classificati…
Recently, the European Commission fined Musk's X platform (…
At the end of 2025, the situation in the Caribbean suddenly…
The U.S. AI industry in 2025 is witnessing a feverish feast…