
Recently, US President Trump signed an executive order announcing a 25% tariff on all imported cars and critical components, which officially came into effect on April 5th. This measure is like a heavy bomb, causing waves in the global automotive industry, and American car companies, as important participants in it, have been fully and deeply influenced.
From a cost perspective, American car companies have suffered a heavy blow. The US automotive industry is deeply integrated into the global supply chain system, and many key components rely on imports. Taking General Motors as an example, about 40% of its vehicles sold in the United States rely on overseas assembly, and core components such as engines mainly come from factories in Mexico and other countries. JPMorgan estimates that General Motors needs to pay up to $13 billion in tariffs annually. Ford is also in a difficult situation, facing an additional cost of $4.5 billion. In addition, Trump's proposed tariff policy on Mexican imports has increased labor costs for American automakers by over $3500 per vehicle. If the production of components returns to the United States, the cost may further increase due to factors such as high labor costs and raw material costs in the United States. These increased costs are like heavy shackles, severely compressing the profit margins of car companies.
In terms of production layout, American car companies are forced to make difficult adjustments. To cope with the impact of tariffs, some car companies have chosen to reduce production and lay off employees. For example, Stellantis plans to lay off employees at five factories in the United States and reduce production lines in Mexico and Canada, as its North American supply chain is highly dependent on Mexican factories. The new tariffs will result in an increase of approximately $4200 in the cost of each vehicle. General Motors plans to increase pickup truck production in Indiana, USA, while reducing production capacity at its Mexico factory. It also plans to hire hundreds of temporary employees at its factory in Fort Wayne, Indiana, and consider arranging overtime to increase production capacity. Although these adjustments are the coping strategies of car companies, they also bring many uncertainties, which may affect production efficiency and product quality, and may also face pressure from labor unions and other aspects during the layoff process.
Market sales have also been impacted. The cost of tariffs will ultimately be passed on to consumers, leading to an increase in car prices. Anderson Economic Group predicts that the cost of imported cars may increase by $3500 to $12200, with electric vehicles experiencing the highest increase due to their dependence on imported components. The average price of new cars in the United States has reached $48500. If it continues to rise by 5% -25%, the pressure on middle-class families to purchase cars will significantly increase. The Peterson Institute warns that rising costs will suppress demand, and it is expected that US car sales may decrease by 3 million units, equivalent to nearly one-fifth of total sales in 2024. The decline in sales is undoubtedly a huge challenge for the revenue and market share of car companies, which may put them in a more disadvantageous position in market competition.
From a long-term development strategy perspective, the US tariff policy has disrupted the global layout rhythm of car companies. The supply chain and production layout originally built by car companies based on global resource optimization and market proximity are facing restructuring due to tariff policies. However, supply chain restructuring is not achieved overnight, and this process takes several years and hundreds of billions of dollars. The US Automotive Policy Committee pointed out that the North American integrated supply chain has been formed for decades, and forced fragmentation will lead to a permanent increase in production costs. During the restructuring process, car companies may find it difficult to quickly find suitable suppliers, facing issues such as component supply interruptions and unstable quality, which in turn affects the speed of new car development and launch, weakening their competitiveness in the global market.
The impact of the tariff war initiated by the United States on American car companies is multifaceted and far-reaching. Although the original intention of the US government may be to protect local industries and promote the return of manufacturing, in reality, it has brought a series of difficulties to American car companies, such as cost surges, chaotic production layouts, hindered market sales, and disrupted development strategies. This also makes people realize that in today's globalized economy, trade protectionist tariff policies are not a good solution to the problem, but may instead cause unexpected harm to domestic industries. How American car companies will seek breakthroughs and development in this complex policy environment in the future is worth continuous attention.
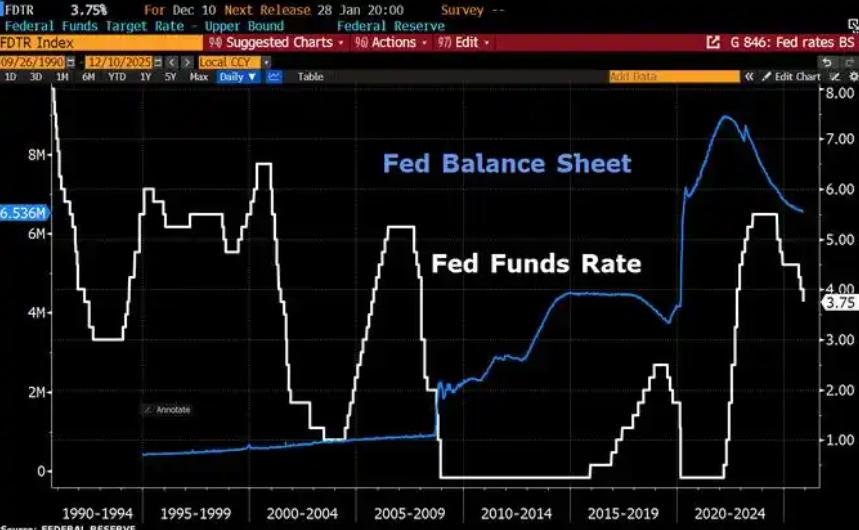
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sheet by $2.4 trillion through quantitative tightening (QT) policies, leading to a near depletion of liquidity in the financial system.
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sh…
On December 11 local time, the White House once again spoke…
Fiji recently launched its first green finance classificati…
Recently, the European Commission fined Musk's X platform (…
At the end of 2025, the situation in the Caribbean suddenly…
The U.S. AI industry in 2025 is witnessing a feverish feast…