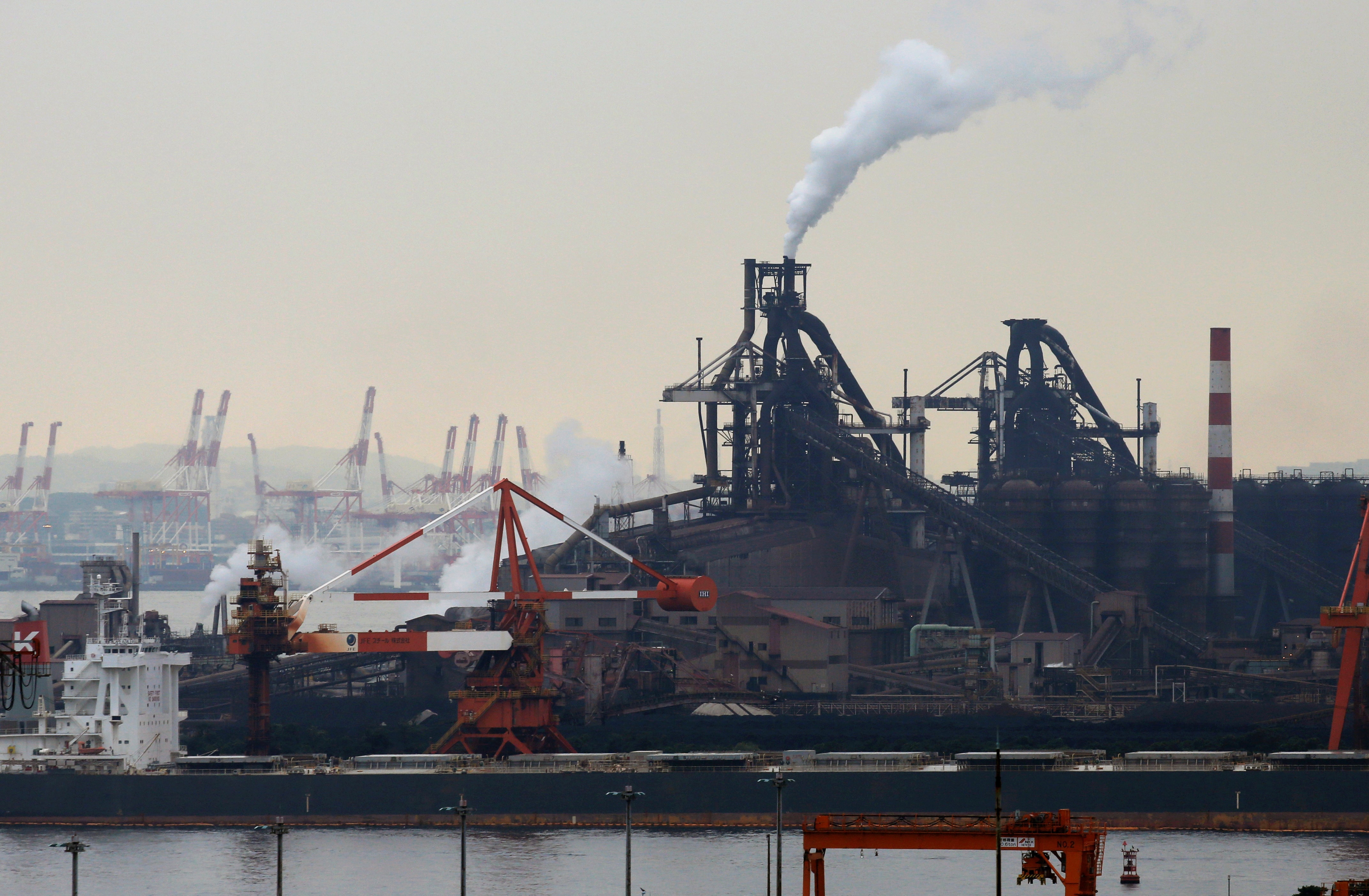

Recently, the Japanese government stated this week that the growth rate of Japan's factory output and exports has fallen far below expectations, and the current situation is attributed to several major factors, primarily the impact of comprehensive U.S. tariffs. Data released by Japan on manufacturing growth reveals that U.S. tariff policies have significantly affected the economic development trends of Asian markets, highlighting the challenges and difficulties faced by the region at this stage. The slowdown in Japan's export growth, which is much lower than market expectations, can be traced back to the tariff escalation policies implemented after Trump took office, which exacerbated global trade tensions—particularly the U.S. tariffs on Asian exports. The increased tariffs have raised costs, thereby affecting sales and profits.
According to the Japanese government, the implementation of U.S. tariff policies has hindered the growth of Japan's manufacturing sector, with particularly severe impacts on exports of automobiles, auto parts, and steel products. Notably, U.S. tariff policies are not limited to Japan but extend to the entire Asian market, exerting a profound influence on the overall economic development of the region. Against the backdrop of tariff barriers and increasing uncertainty in global trade, maintaining stable economic growth has become a critical challenge for Asia at this stage.
With the deepening of globalization, Asian markets now play a pivotal role in the global economy. The implementation of U.S. tariffs undoubtedly poses a significant challenge to the region. The impact of these tariffs has hindered economic development in Asia, while the rise in trade barriers has exacerbated market and trade issues. In response, Asian markets must promptly adjust their strategies to adapt to the changing trade environment caused by U.S. policies.
Amid increasing tariff barriers, Asian markets should actively explore new markets to reduce reliance on the U.S. and avoid being overly dependent on a single market. Additionally, they should optimize product structures in line with U.S. tariff policies and shifting market demands. For products severely affected by tariffs—either due to soaring costs or plummeting demand—production scales should be appropriately reduced, with resources redirected toward products with greater market potential and demand. This will help businesses adapt to market changes and sustain profitability.
Furthermore, Asian markets should not passively endure the impact of U.S. tariffs but must also adopt countermeasures. For instance, when the U.S. announced a 125% tariff hike on Chinese goods, China responded by imposing retaliatory tariffs on key U.S. materials. This not only serves as a response to U.S. policies but also underscores the importance of safeguarding national interests in international trade.
In conclusion, strengthening regional cooperation is an effective measure for Asian markets to counter the challenges posed by U.S. tariffs. By enhancing economic collaboration among Asian nations—through resource sharing, complementary advantages, and joint efforts to withstand tariff pressures—the region can better navigate these challenges. Additionally, cooperation in technological R&D, talent development, and industrial innovation will bolster resilience against external shocks.
Since 2025, the conflict between the United States and Europe over the governance of the digital economy has continued to escalate.
Since 2025, the conflict between the United States and Euro…
When German Chancellor Mertz officially announced that he w…
On December 3rd local time, the copper price on the London …
The European Commission announced a new economic security s…
The European Commission announced a new economic security s…
For nearly a year, US President Donald Trump has launched a…