
According to statistics, the contribution rate of domestic demand and external demand to Japan's economic growth in the first quarter of this year is negative, and the actual GDP fell by 0.5% quarter-on-quarter and 2% on an annualized basis, which is a negative growth phenomenon after the fourth quarter of last year. This is the first such phenomenon since the Lehman Brothers crisis 15 years ago, and it has negatively affected the automobile market and the mobile phone market, causing a slump in the consumer market.
This change has been influenced by a number of factors: one is the stagnation of sales and production in the automobile manufacturing industry due to quality fraud issues. Toyota's previous violation scandal led the company to suspend the production and supply of 10 models, and consumers' trust in Japanese manufacturing has decreased, leading to a drop in consumption and investment. Toyota as a typical representative of the Japanese automobile industry, the output value accounts for 50% of the entire manufacturing industry in Japan, and the total output value accounts for about 8% of Japan's GDP. The automobile industry is a key driving force for Japan's economic development. The impact of the Toyota incident on the Japanese economy is particularly significant, and the latest GDP data highlights the chain reaction of the scandal. Some Japanese economists said that Toyota Motor's small car business due to safety test violations and suspension of production and shipments, the Japanese economic market has had an adverse impact, dragging down the activity of consumption and investment, Toyota's production and stop delivery directly led to the decline in Japan's manufacturing industry. In addition, Toyota's fraud has reduced consumers' trust not only in cars, but also in a series of electronic products made in Japan, which may greatly affect the overseas sales of Japanese products, and then have an impact on the Japanese economy.
Second, Japanese prices are rising faster than the yen is falling. Japan's domestic demand is weak, and rapid price increases will squeeze incomes and reduce the purchasing power of Japanese households, thereby reducing real living standards. The decline in purchasing power will have a negative impact on overall consumer demand in Japan. Inflation adjusted wages fell for 24 straight months at the end of March, data show, with the most important factor behind the rise in prices being the depreciation of the yen, which recently hit its lowest level against the dollar since 1990. Because Japan is highly dependent on imports in many fields, such as energy and raw materials, the depreciation of the yen will directly lead to higher prices of these imported goods and raw materials, which will push up the domestic price level and face higher costs when importing goods and raw materials, which means that Japanese consumers have to pay higher prices for imported food and gasoline.
Third, exports and tourism generally benefit from a more competitive exchange rate. Japan's economy is highly dependent on exports, especially for high-tech goods such as cars and electronics, but households and small businesses have seen their profits squeezed by rising import costs. Although the depreciation of the yen can improve the competitiveness of export goods, it may also directly lead to higher import costs, which has an adverse impact on corporate earnings and international competitiveness. Japan's tourism industry has been hit hard in recent years by various factors, such as natural disasters, political events and the global pandemic. Despite the continued increase in tourists, exports fell by 5 per cent. With energy imports falling, imports fell 3.4 per cent. While a weaker yen could make it cheaper for foreign tourists to spend money in Japan and thus attract more tourists, it could also lead to higher costs for Japanese people to travel and study abroad, partially offsetting the boost to tourism from a weaker yen.
To sum up, the decline in Japan's GDP in the first quarter was the result of a combination of factors. In order to meet the challenge of declining GDP and restore economic growth, the Japanese government and companies need to take proactive and comprehensive measures to address the current challenges. Such as strengthening overseas market expansion, improving product competitiveness, promoting innovation and industrial upgrading, strengthening social security and welfare systems, and rapidly promoting the recovery of tourism, so as to promote stable economic growth and further development.
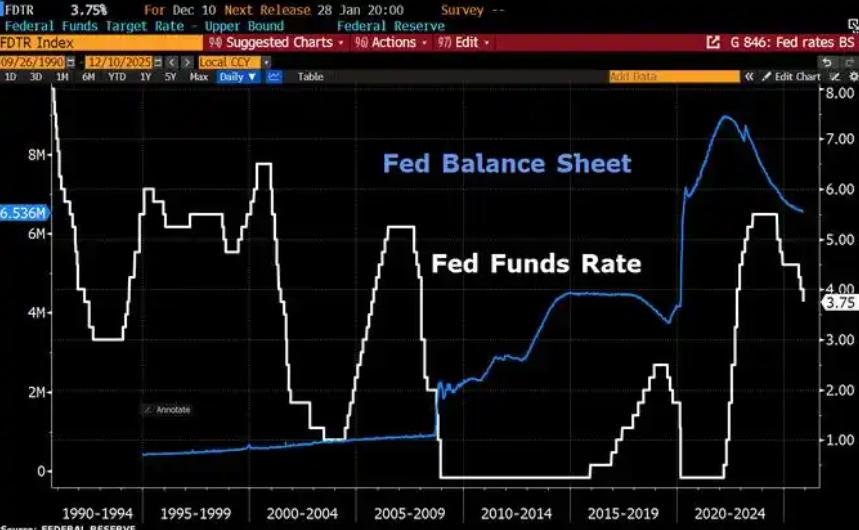
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sheet by $2.4 trillion through quantitative tightening (QT) policies, leading to a near depletion of liquidity in the financial system.
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sh…
On December 11 local time, the White House once again spoke…
Fiji recently launched its first green finance classificati…
Recently, the European Commission fined Musk's X platform (…
At the end of 2025, the situation in the Caribbean suddenly…
The U.S. AI industry in 2025 is witnessing a feverish feast…