
The Japanese government recently stated that from January to March this year, the Japanese economy contracted at an annual rate of 2.0%, marking the first contraction in two quarters. The main reason for this situation is that domestic demand has been hit by rising inflation and the suspension of car shipments due to the safety testing scandal at Dafa Automobile Company. After adjusting for inflation, the real gross domestic product (GDP) in the first quarter of 2024 decreased by 0.5% month on month, and GDP often represents the total value of goods and services produced by a country.
Firstly, according to economists surveyed by the Japan Economic Research Center, the actual annual economic rate is expected to shrink by 1.17%, which is more severe than the 0.29% contraction in the previous quarter. This situation is widely expected, and the economy is expected to rebound in the quarter of April to June. However, this data also indicates that the Bank of Japan is facing difficulties in raising interest rates again in response to the prospects of slow economic growth, inflation, and a weak yen. The weak GDP data reveals the negative impact of the yen's decline, and it cannot be ruled out that the Bank of Japan may face pressure to further tighten policies to cope with the yen's weakness.
Secondly, according to the Japanese Cabinet Office, private consumption, which accounts for more than half of the economy, has decreased by 0.7%, marking the fourth consecutive quarter of decline. The longest consecutive decline in 15 years highlights the weakness of domestic demand, which is a key factor in strengthening the virtuous cycle of wage and price increases in Japan. This will enable the Bank of Japan to reduce its monetary stimulus measures maintained in the fight against long-term deflation. Due to inflation caused by factors such as rising crude oil prices and weak yen, as of March, Japanese households will pay an additional 106000 yen or more. Saisuke Sakai, Senior Economist at Mizuho Research Technology Co., Ltd., said, "When real wage growth remains negative, it is difficult to expect strong private consumption. Even without the latest car scandal, Japan's GDP growth can only be around zero at most."
In addition, weak domestic demand and inflation exceeding wage growth occur simultaneously. Despite major companies weighing the impact of the recent round of cost driven inflation and agreeing to pay increases, the spring annual wage negotiations between unions and management achieved the best results in thirty years, but this situation still occurred. For sustained wage growth, corporate profits are crucial. Small and medium-sized enterprises must provide higher wages to alleviate labor shortages, but the weak yen is becoming a resistance. The same applies to service providers.
Furthermore, in terms of the domestic economy, the automotive industry is a key driving force for the Japanese economy and plays an important role in the domestic economy. The latest GDP data highlights the chain reaction of the scandal, affecting consumer and business spending as well as exports. Despite the continuous growth of inbound tourism, exports still decreased by 5.0%. Due to a decrease in energy imports, imports have decreased by 3.4%. Japan has benefited from the recovery of its inbound tourism industry, partly due to the depreciation of the Japanese yen, which has made travel and consumption for foreign tourists to Japan cheaper. Their expenditures are counted as exports in GDP data.
Overall, the Japanese economy is currently facing severe challenges, which are the result of the combined action of multiple structural factors. Although Japan ended its negative interest rate policy in March this year, there are still disagreements within the Bank of Japan regarding interest rate hikes, fearing that raising rates too quickly may have unnecessary impacts on the economy. Considering the fragility of the Japanese economy, it is expected that the Bank of Japan will adopt a more cautious and conservative monetary policy, closely monitoring changes in economic data, inflation trends, external economic environment, and so on.
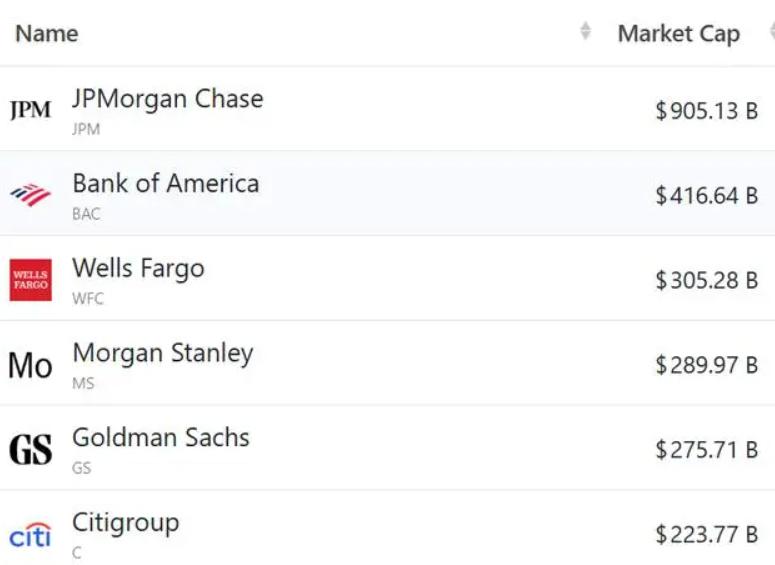
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financial regulations and the recovery of investment banking business, the market value of the six major banks in the United States has cumulatively increased by approximately 600 billion US dollars by 2025.
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financia…
On Christmas evening, U.S. President Trump posted on social…
According to multiple foreign media reports, the recent fin…
The middle class, once regarded as the cornerstone of Ameri…
On December 19th local time, the US military launched a lar…
The Boxing Day sunshine should have cast a false glow of pr…