
Yesterday, the British Retail Consortium (BRC) warned that food prices were expected to rise by an average of 4.2 per cent in the second half of the year, putting more pressure on local households as consumers face soaring water bills, council tax and energy bills. The British Retail Consortium is an authoritative organization representing the interests of the British retail industry, and the information it releases has high credibility and authority. The association blamed the rise in food prices on Chancellor Reeves' autumn Budget in October 2024, which it said many businesses believed would have a negative impact on investment, jobs and pay. UK retailers face £7 billion in additional costs by 2025, which could eventually be passed on to consumers, leading to higher food prices. UK Chancellor of the Exchequer Reeves' Autumn Budget in October 2024 was also an important factor in the rise in food prices. The budget includes the largest tax increases in 30 years, putting economic pressure on businesses and consumers alike.
The BRC's forecast results have complex and multi-faceted implications for business, including for retailers, who may need to adjust their product mix, assess pricing and marketing strategies to address the challenges and trends posed by rising food prices. For example, increasing the proportion of high value-added food products, or engaging consumers through promotional activities. Higher prices can lead to changes in consumer buying behavior, and retailers need to manage inventory more finely to avoid overstocking or stock shortages. Facing the pressure of rising food prices, retailers need to pay more attention to cost control, including procurement, inventory, logistics and other aspects of optimization, in order to reduce operating costs. Rising food prices could lead to changes in the competitive landscape of the market. Some retailers may gain market share by offering more competitive prices or better service to attract consumers. At the same time, retailers need to strengthen communication with consumers, explain the reasons for price increases, and offer alternatives or value propositions to maintain consumer trust and loyalty.
The second is the impact on the supply chain, rising food prices may increase the cost of the supply chain, including raw material procurement, transportation and warehousing costs. That could lead suppliers to raise prices, which could put pressure on retailers' margins. Suppliers may need to reassess their pricing strategies to cope with the impact of rising raw material costs and changes in market demand. In order to reduce costs and improve efficiency, suppliers may strengthen supply chain management, including optimizing production processes, improving production efficiency, and strengthening quality control. In the face of market opportunities brought about by rising food prices, suppliers may actively seek new market expansion opportunities to expand their business scope and increase revenue sources. At the same time, there needs to be more cooperation between retailers and suppliers to jointly address the challenges posed by rising prices. It may be necessary to renegotiate the terms of the contract to ensure that both parties can withstand the cost pressures.
Third, the impact on consumers, rising food prices may lead to a decline in consumer purchasing power, especially low-income households. They may spend less on food or opt for cheaper alternatives. Consumers may change their spending habits, such as paying more attention to price, choosing more affordable food combinations or brands, and eating out less often. Rising food prices can lead to changes in consumer loyalty to brands. If a brand can offer more competitive prices or better service, consumers may be more inclined to choose that brand.
The fourth is the impact on the economy. Rising food prices may exacerbate inflationary pressures and have a negative impact on the overall economy. This could lead to a decline in consumer confidence, which in turn could affect consumption and investment. The government may take a series of policy measures to mitigate the negative impact of rising food prices, such as providing subsidies, lowering taxes, and strengthening market supervision. These policy changes may have some impact on the business sector.
To sum up, the BRC's forecast that food prices in the country will rise by 4.2% in the second half of the year will have a multi-faceted impact on the business sector. Retailers, suppliers and consumers all need to pay close attention to market dynamics and policy changes and take timely measures to address these impacts.
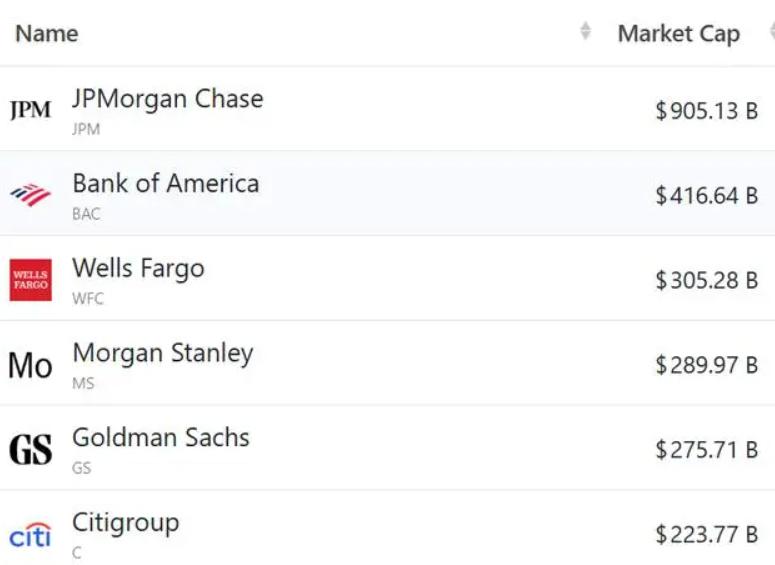
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financial regulations and the recovery of investment banking business, the market value of the six major banks in the United States has cumulatively increased by approximately 600 billion US dollars by 2025.
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financia…
On Christmas evening, U.S. President Trump posted on social…
According to multiple foreign media reports, the recent fin…
The middle class, once regarded as the cornerstone of Ameri…
On December 19th local time, the US military launched a lar…
The Boxing Day sunshine should have cast a false glow of pr…