
According to preliminary data from the May monthly labor survey released by the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, the per capita real wage in Japan has decreased by 1.4% compared to the same period last year, after excluding the impact of price changes. This data reflects the current economic situation and changes in the labor market in Japan.
The decline in real wages may be caused by various factors, including but not limited to slowing economic growth, declining corporate profitability, rising labor costs, inflation, etc.
Firstly, the significant increase in food and energy prices is one of the main reasons for the decline in real wages. Although nominal wages have increased in some areas, they have not kept up with the pace of inflation, resulting in a decrease in real purchasing power. Apart from rising food and energy prices, prices of other goods and services may also rise, further compressing real wages. In addition, the uncertainty of inflation may lead both businesses and consumers to adopt more conservative financial strategies, affecting economic growth and wage growth.
Secondly, global economic uncertainty has increased, Japan's economic growth has slowed down, and corporate profitability has been limited, thereby affecting wage growth. Due to cautious considerations, companies are generally unwilling to significantly increase wages. The slowdown in economic growth not only affects the profitability of enterprises, but may also lead to a decrease in employment opportunities, especially for young people and informal employees. In this case, even if nominal wages increase, actual wages may decrease due to reduced employment opportunities.
Then, the proportion of informal employment in the Japanese labor market is relatively high, and these employees usually enjoy lower wages and fewer benefits, further lowering the overall actual wage level. The universality of informal employment not only affects wage levels, but may also lead to job instability and affect long-term income growth for employees. In addition, informal employees may lack union representatives and find it difficult to raise wages through collective bargaining.
Once again, Japan's severe aging population has led to a tight labor market, affecting wage levels and increasing pressure on social security expenditures. The aging population not only affects the labor market, but may also lead to an increase in healthcare and elderly care expenditures, further increasing the financial burden on the government. In this situation, the government may find it difficult to provide sufficient support to raise wage levels.
Finally, global supply chain disruptions and international trade tensions have also had a negative impact on the production and exports of Japanese companies, thereby limiting their ability to raise wages. Global supply chain disruptions and international trade tensions not only affect the production and exports of enterprises, but may also lead to price increases in raw materials and intermediate products, further driving up inflation and affecting real wages.
For the Japanese government and relevant policy makers, this data may be a warning signal that they need to pay attention to and take measures to improve the conditions of the labor market and increase the actual income of the people. This may include measures such as promoting economic growth, optimizing tax policies, improving labor productivity, and controlling inflation. Although the Japanese government has taken a series of measures to cope with the decline in real wages and inflationary pressures, the effectiveness remains to be seen. In the short term, the global economic environment, policy implementation efforts, and the reactions of businesses and consumers will become key factors. In the long run, addressing population aging and structural issues in the labor market remains a major challenge for the Japanese economy.
Meanwhile, this data may also have an impact on the consumption behavior and savings willingness of the Japanese people. The decline in real wages may lead to consumers reducing their purchases of non essential goods and increasing savings to cope with potential economic uncertainty.
With the emergence of new economic data and policy effects, whether Japan can effectively curb the trend of declining real wages and alleviate inflationary pressures will become a focus of attention in the future. The joint efforts of the government, enterprises, and all sectors of society will play a crucial role in this process.
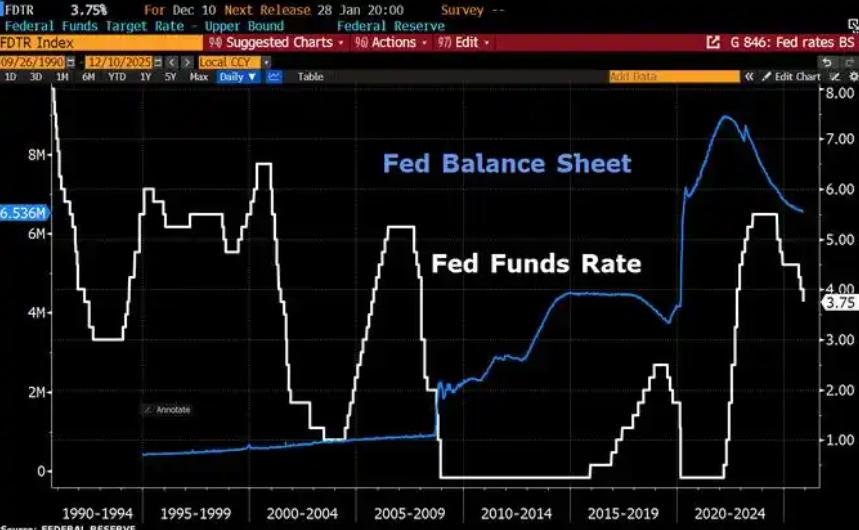
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sheet by $2.4 trillion through quantitative tightening (QT) policies, leading to a near depletion of liquidity in the financial system.
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sh…
On December 11 local time, the White House once again spoke…
Fiji recently launched its first green finance classificati…
Recently, the European Commission fined Musk's X platform (…
At the end of 2025, the situation in the Caribbean suddenly…
The U.S. AI industry in 2025 is witnessing a feverish feast…