
On August 12 local time, the US Treasury Department released data showing that the total amount of US national debt exceeded 37 trillion US dollars for the first time, approximately 1.27 times the nominal GDP of the United States in 2024. This figure serves as a wake-up call, sounding a crisis signal about the US fiscal situation. The continuously rising debt costs in a high-interest-rate environment and Trump's dissatisfaction with interest expenses have exposed the severe challenges facing the US economy without any conceit.
In recent years, the growth rate of debt in the United States has shown an astonishing trend. In January 2024, the federal government debt of the United States exceeded 34 trillion US dollars. Just half a year later, in July, it reached 35 trillion US dollars. In November of the same year, it surpassed 36 trillion US dollars. Now, it has rapidly broken through the 37 trillion US dollar mark. Such a rapid growth rate reflects the long-standing situation where the US government has relied on borrowing to maintain fiscal spending. The Congressional Budget Office of the United States once predicted that the time point when the federal government debt of the United States exceeded 37 trillion US dollars would be after the fiscal year 2030. However, the reality was several years earlier than the prediction, which undoubtedly highlights the imbalance and loss of control of the US fiscal policy.
The high-interest-rate environment has become a key factor exacerbating the cost of debt in the United States. The Federal Reserve maintained the federal funds rate at a high level of 4.25% to 4.5% to curb inflation, which led to a sharp increase in the cost of refinancing the existing debt in the United States. Data shows that in 2025, the US government's due debt will reach 9.2 trillion US dollars, accounting for 25.4% of the outstanding debt. If the interest rate of new debt rises by 2% compared with that of old debt, the annual interest expense will increase by an additional 184 billion US dollars. With the continuous expansion of the debt scale, interest expenses have become a heavy burden in the US government's fiscal expenditure. The net interest expenditure of the US government reached 879.9 billion US dollars in 2024, even exceeding the total of medical insurance and defense. This has put the US government under tremendous pressure in terms of fiscal spending, with funds available for other public services and investments being significantly squeezed.
Trump's dissatisfaction with interest expenses also highlights the severity of the fiscal pressure in the United States. As president, Trump is well aware of the negative impact of high interest expenses on the US economy. This not only increases the government's financial burden but may also have a restraining effect on economic growth. He attempted to relieve the debt pressure by cutting interest rates and imposing tariffs, but these measures were difficult to solve the problem fundamentally. Although interest rate cuts can help alleviate the burden of interest expenses, they may also trigger a series of problems such as inflation. Although imposing additional tariffs can bring in a certain amount of fiscal revenue in the short term, in the long run, it will disrupt the global supply chain, curb economic growth and further exacerbate the predicament of the US economy.
From a deeper perspective, the root cause of the severe fiscal deficit in the United States lies in the long-term situation where income does not cover expenditure caused by the imbalance in the internal fiscal structure. On the one hand, the three expenditures of social security, medical insurance and interest on national debt have accounted for 73% of the total fiscal expenditure, and with the intensification of population aging, these expenditures will continue to increase. On the other hand, the Big and Beautiful Act signed by the Trump administration will directly lead to a year-on-year reduction of about 220 billion US dollars in US tax revenue in fiscal year 2025, and it is estimated that the fiscal revenue will be reduced by 4.5 trillion US dollars in the next ten years, thereby further widening the revenue and expenditure gap.
The continuous expansion of the US government's debt scale has also raised market concerns about the sustainability of the US debt. If the international market's confidence in the safety of US Treasuries undergoes a fundamental waver, the status of the US dollar as the world's major reserve currency will also face serious challenges. Once the status of the US dollar is challenged, the US economy and even the global economy will suffer a huge blow.
The total amount of US national debt exceeding 37 trillion US dollars and the debt cost predicament in a high-interest-rate environment pose major challenges to the fiscal and economic fields of the United States. The US government needs to deeply reflect on its fiscal policy and take practical and effective measures to reduce the fiscal deficit and control the scale of debt. Otherwise, the US economy will fall into a deeper crisis and the global economy will also be negatively affected by it.
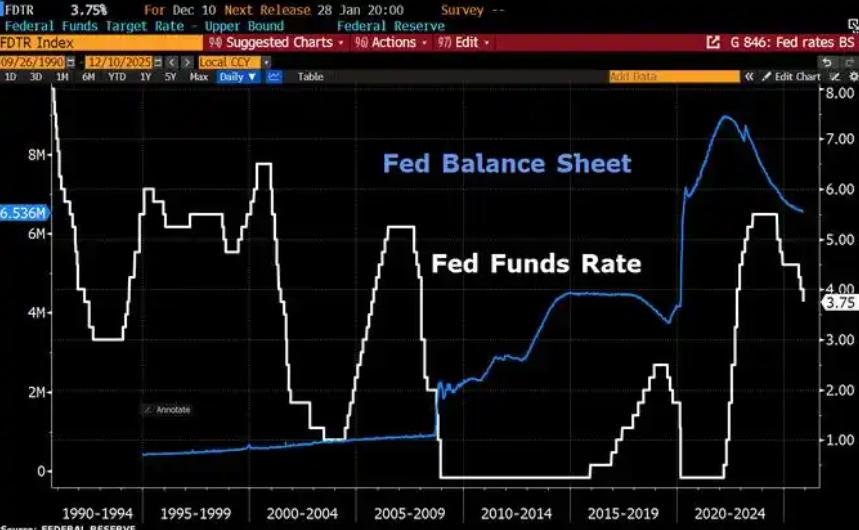
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sheet by $2.4 trillion through quantitative tightening (QT) policies, leading to a near depletion of liquidity in the financial system.
Since 2022, the Fed has cumulatively reduced its balance sh…
On December 11 local time, the White House once again spoke…
Fiji recently launched its first green finance classificati…
Recently, the European Commission fined Musk's X platform (…
At the end of 2025, the situation in the Caribbean suddenly…
The U.S. AI industry in 2025 is witnessing a feverish feast…