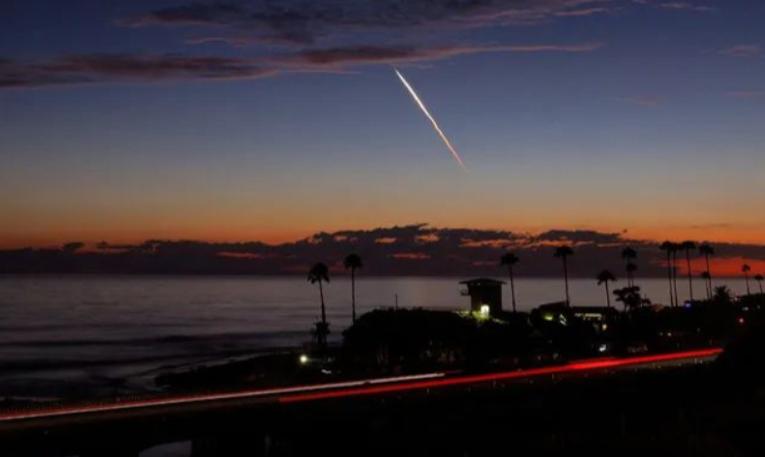

Recently, a series of Starlink satellites launched by SpaceX, an American entrepreneur, have fallen to Earth one after another, attracting widespread attention. A study jointly released by the University of Maryland and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in the United States pointed out that due to the intensified solar activity, Starlink satellites are falling into the Earth's atmosphere much faster than expected. The research team analyzed the orbital data of 523 Starlink satellites from 2020 to 2024 and discovered a worrying trend: during intense geomagnetic storms, these satellites fall into the Earth's atmosphere at a speed far exceeding expectations. The researchers also stated: "Our results indisputably show that the stronger the geomagnetic activity, the faster the satellites fall." In response to this phenomenon, the research team led by physicist Danny Oliveira from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center analyzed that the satellite fall is indeed clearly related to solar activity. The significant increase in solar activity shortens the operating time of Starlink satellites in orbit, causing them to fall faster.
The large-scale fall of Musk's Starlink satellites this time has not only affected the operation of low-orbit satellites but also had a significant impact on the technology and aerospace fields. Firstly, it has an impact and challenge on aerospace technology. Starlink satellites operate at an orbit of about 550 kilometers, although they can provide low-latency global internet services, they expose fatal flaws during solar activity peaks. The expanding atmosphere increases the satellite's flight resistance by more than 50%, and some test satellites even reach as low as 210 kilometers, almost flying along the edge of the atmosphere. This requires future satellite designs to enhance anti-interference capabilities and orbit planning to more accurately assess the impact of space weather. The shortened satellite lifespan forces SpaceX to accelerate the launch of new satellites to fill the gaps, with the launch frequency increasing by 30% compared to the previous year, and fuel and maintenance costs soaring. The capital market reacted quickly, with Tesla's stock dropping by 8% within a week after the fall incident was exposed. Investors were worried that the profitability of Starlink was overestimated. The International Astronomical Union warned that 42,000 Starlink satellites would form a "light pollution wall" in the night sky, preventing telescopes from capturing the faint light of distant galaxies. When the first batch of Starlink satellites were launched in 2019, the Hubble Telescope was forced to discard multiple photos due to the satellite's trajectory.
Secondly, it has an impact on technological cooperation and rules. The fall of Starlink satellites exposed the shortcomings of current space rules, prompting the international community to accelerate the formulation of the "International Management Rules for Giant Constellations", requiring satellites to be equipped with enhanced radiation protection armor and 100% combustible structures, and further promoting the reform of the "First to Claim" rule of the International Telecommunication Union. This incident has prompted countries to re-evaluate satellite design standards, requiring in-orbit satellites to have stronger anti-interference capabilities and orbit maintenance capabilities, and promoting the establishment of a space debris monitoring and warning system to reduce collision risks.
Thirdly, it has an impact on the technology industry and market competition. The large-scale fall of Starlink satellites exposed the technical shortcomings of satellites in responding to changes in the space environment, such as insufficient orbit maintenance capabilities and insufficient prediction of the impact of solar activity. This has prompted the aerospace technology industry to re-examine satellite design standards, requiring satellites to have stronger anti-interference capabilities and orbit maintenance capabilities, and promoting the research and development and improvement of related technologies. The large-scale fall of Starlink satellites may affect users' trust in its services, thereby affecting market share. Competitors may take this opportunity to expand market share, promoting intensified market competition. At the same time, this also prompts other satellite internet projects to accelerate technological research and market expansion to seize market opportunities. In conclusion, the large-scale fall of Starlink satellites has profoundly exposed the systemic challenges faced by current aerospace technology in terms of technical reliability, space environment management, and market operation. Only through technological innovation, international collaboration, and rule upgrading can the aerospace field achieve sustainable development while ensuring safety.
Since 2025, the conflict between the United States and Europe over the governance of the digital economy has continued to escalate.
Since 2025, the conflict between the United States and Euro…
When German Chancellor Mertz officially announced that he w…
On December 3rd local time, the copper price on the London …
The European Commission announced a new economic security s…
The European Commission announced a new economic security s…
For nearly a year, US President Donald Trump has launched a…