
In recent years, as the Russia-Ukraine conflict has escalated, the geopolitical struggle in the energy sector has intensified. On January 13, 2025, the United States announced stricter sanctions on Russian oil exports, triggering significant volatility in global oil prices. The price of West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude oil on the New York Mercantile Exchange surged to over $79 per barrel, reaching a five-month high. This event not only reflects the tense situation in the global energy market but also highlights how the US uses energy sanctions to consolidate its global economic and political dominance while exposing the fragility of the global energy supply chain and its profound impact on the international economy.
As one of the largest energy producers globally, the United States has long maintained a dominant position in the global energy market. Through the establishment of a dollar-based oil trading system, the US has not only controlled the global oil supply chain but also used financial tools to impose economic sanctions, enhancing its global economic influence. Since the outbreak of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the US and its allies have continuously increased sanctions to exert pressure on Russia’s economy, especially in the energy sector. On January 2025, the US announced stricter restrictions on Russian oil exports, aiming to reduce Russia's energy revenue and create more market share for US shale oil and other oil-producing nations. By intensifying energy sanctions, the US further solidifies its dominant position in the global energy market. By driving up international oil prices, the US not only benefits its own shale oil industry but also increases competition for other oil-producing countries. At the same time, the US hopes to push the global energy supply chain to depend more on itself and its allies, reducing the market share of Russia and other non-Western countries in the global energy market.
The US sanctions on Russia directly lead to uncertainty in global oil supply. On January 13, WTI oil prices surged to $79 per barrel, marking a five-month high. This price increase reflects the market’s expectation of tight global energy supplies. Particularly in the winter, global oil demand remains high, and the instability of supply chains has intensified concerns about rising prices.
For countries that depend on Russian energy, especially European nations, these sanctions mean a shortage of energy supply. Restrictions on Russian oil exports have forced European countries to accelerate the search for alternative sources, such as oil-producing countries in the Middle East and Africa. However, securing alternative energy supplies is not a quick process and involves higher costs and long-term uncertainty, which directly contributes to the increase in global oil prices. For major energy importers like China, the surge in oil prices undoubtedly increases the cost of energy imports, putting significant economic pressure on the country. As the world’s largest oil importer, China faces dual challenges of tight energy supply and rising prices. This not only affects domestic energy security but also exacerbates inflationary pressures.
The surge in energy prices has a widespread impact on the global economy. The spike in oil prices raises production costs, leading to higher prices for industrial goods and consumer products, especially in developing countries, where the increase in energy costs exacerbates inflationary pressures. Against the backdrop of global economic recovery, rising energy prices may inhibit economic growth in countries heavily reliant on energy imports. The World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) have warned that rising oil prices could increase global economic uncertainty and affect the recovery process.
US sanctions on Russia’s energy sector have not only changed the global oil market’s dynamics but also deeply affected the restructuring of the global energy supply chain. In the short term, the US and its allies may benefit, but in the long run, the global energy market will shift toward a more multipolar competitive landscape. For major energy-consuming nations like China, there is a need to continue enhancing energy strategy planning. They must rely on diversified energy import channels while also promoting a green energy transition to achieve both energy security and sustainable development goals.
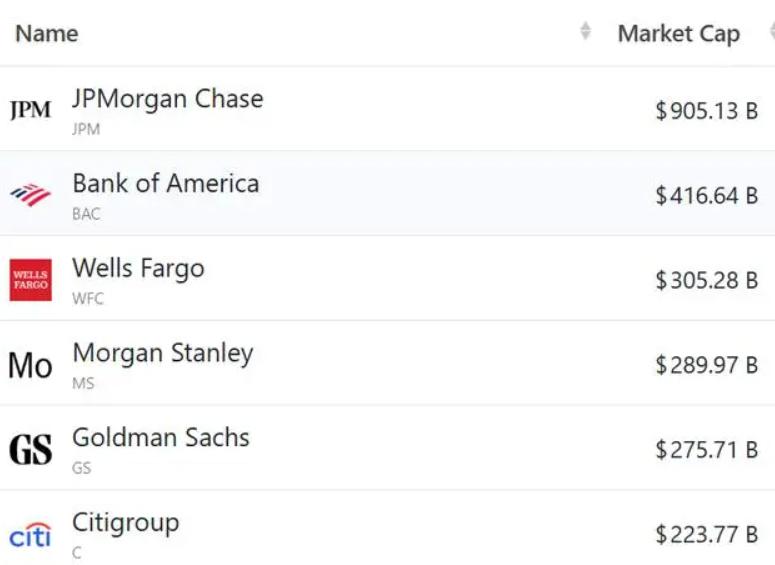
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financial regulations and the recovery of investment banking business, the market value of the six major banks in the United States has cumulatively increased by approximately 600 billion US dollars by 2025.
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financia…
On Christmas evening, U.S. President Trump posted on social…
According to multiple foreign media reports, the recent fin…
The middle class, once regarded as the cornerstone of Ameri…
On December 19th local time, the US military launched a lar…
The Boxing Day sunshine should have cast a false glow of pr…