
The record-breaking 36-day shutdown of the US government is causing turmoil in global financial markets through abnormal fluctuations in the Treasury's General Account (TGA). This core fiscal account held by the Federal Reserve showed a "only in, no out" damming lake effect during the shutdown. The balance soared from the regular 300 billion US dollars to 1 trillion US dollars, equivalent to withdrawing 700 billion US dollars of liquidity from the market. Its tightening effect was comparable to the quantitative tightening (QT) policy actively implemented by the Federal Reserve. It has brought multiple chain reactions to the US economy and the global financial system.
The liquidity siphon effect of the TGA account stems from the fiscal revenue and expenditure imbalance during the shutdown period. Tax revenue and other funds have been continuously flowing into the account, but regular expenditures such as social security payments and government procurement have been forced to suspend due to the government shutdown, resulting in a backlog of funds. Unlike commercial bank deposits, TGA account funds are directly deposited with the Federal Reserve and are out of the physical circulation field. A sharp increase in their balance means a direct reduction in the market's disposable funds. This passive liquidity contraction, in combination with the Federal Reserve's proactive balance sheet reduction, has led to a significant intensification of liquidity tightness in the banking system as of November 6th. The reserve funds of US banks have dropped to 2.85 trillion US dollars, below the 10% safety bottom line of GDP.
The chain reaction in the financial market is equally intense. The US stock market witnessed a significant adjustment under the liquidity shock, with technology stocks and other sectors that are highly sensitive to capital leading the decline. After collectively coming under pressure, the stock markets in the US, Japan and South Korea only managed to rebound slightly. As a "barometer" of risky assets, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin were the first to suffer heavy setbacks, and the market regards them as the "most sensitive victims" under the liquidity crunch. Behind this fluctuation lies a strong correlation between the balance of TGA accounts and asset prices. Historical data shows that during the debt ceiling crisis in 2023, when the balance of TGA accounts dropped to around 50 billion, the Nasdaq 100 Index (QQQ) once pulled back by 10%, while the release of TGA balances in 2020 drove the index to rise significantly.
The monetary policy operations of the Federal Reserve are falling into a passive predicament. The originally ongoing balance sheet reduction plan is facing adjustment pressure due to the liquidity crisis. The market generally expects that the Federal Reserve may be forced to stop the balance sheet reduction earlier. To ease liquidity tightness, the Federal Reserve has resumed the temporary Repo operation (Overnight Repo) since the repo crisis in 2019, injecting nearly $30 billion of liquidity into the market. This passive liquidity injection contradicts the active contraction caused by the government shutdown, distorting the policy transmission mechanism of the Federal Reserve. As a result, the balance sheet expansion plan planned to be launched in early December has added more uncertainties.
The core game in the current market focuses on the end point of the government shutdown. Goldman Sachs, Citigroup and other institutions predict that a temporary funding agreement is expected to be reached in the second week of November, and the government shutdown may come to an end. Once the shutdown ends, TGA accounts will resume spending, and funds from social security payments, government procurement, etc. will flow back into the market. Bank reserves are expected to rise, and lending rates, mortgage costs, and financing costs for securities firms will decline accordingly, providing impetus for the valuation repair of risky assets. Historical experience shows that when the TGA account released liquidity from a high of 1.6 trillion US dollars in 2020, it drove the technology stock index to rise significantly. The market is now expecting a similar liquidity reflux effect.
However, potential risks still cannot be ignored. If the bipartisan game persists and the shutdown is prolonged, the liquidity crunch may evolve from a short-term shock to a long-term pressure, and even trigger credit contraction and a slowdown in economic recovery. Even if the shutdown ends, the pace and scale of the release of funds in the TGA account remain uncertain. Coupled with the lagging effect of the Fed's policy shift, the market may face the continuous challenge of a "tight balance". For global investors, this liquidity crisis triggered by political games once again highlights the systemic risk of the imbalance between the US fiscal policy and monetary policy.
The expansion of TGA accounts triggered by the US government shutdown is essentially a typical case of the transmission of political games to the economic field. The $700 billion liquidity siphon not only tests the resilience of the US financial market but also poses unprecedented challenges to the policy regulation of the Federal Reserve. As expectations of the end of the shutdown rise, the market is entering a critical window period for liquidity restoration. However, the problems of lax fiscal discipline and lack of policy coordination exposed by this crisis may become potential risks affecting the long-term stability of the US economy. The global market needs to be vigilant about the aftereffects of liquidity fluctuations and the chain reaction of such passive tightening on the global economic recovery.
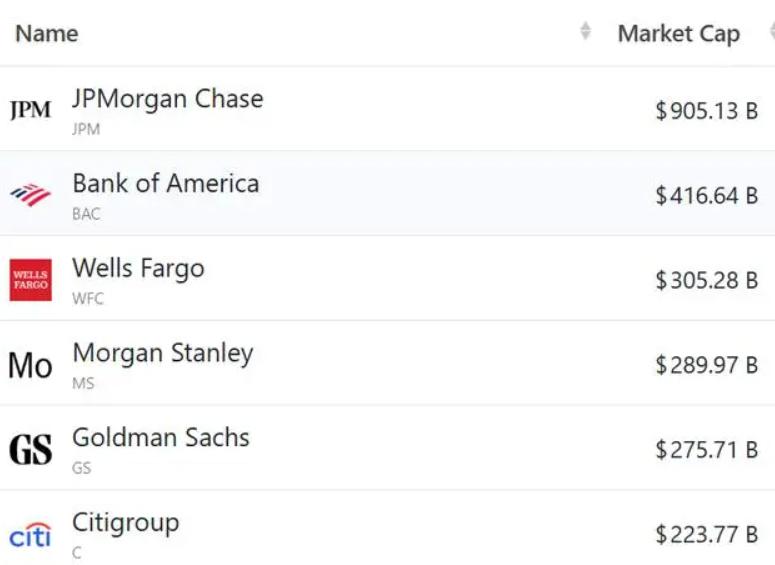
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financial regulations and the recovery of investment banking business, the market value of the six major banks in the United States has cumulatively increased by approximately 600 billion US dollars by 2025.
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financia…
On Christmas evening, U.S. President Trump posted on social…
According to multiple foreign media reports, the recent fin…
The middle class, once regarded as the cornerstone of Ameri…
On December 19th local time, the US military launched a lar…
The Boxing Day sunshine should have cast a false glow of pr…