
Recently, the price turmoil in the Japanese vegetable market has caused a lot of attention. According to multiple data shows that in mid-January 2025, the retail price of Japanese cabbage (cabbage) soared to 3.3 times that of previous years, which undoubtedly brought no small impact to the lives of the Japanese people.
First, we have to focus on the immediate cause of the surge in vegetable prices - poor harvests due to lack of rainfall. As a country with a significant monsoon climate, rainfall is crucial to agricultural production. However, since the summer of 2024, many parts of Japan have suffered from the double whammy of hot summer and insufficient rainfall, which has seriously affected the growth and production of vegetables. In particular, cabbage and other leafy vegetables, the demand for water is particularly strong, once the rainfall is insufficient, the production is bound to decline significantly. According to data released by the Japanese Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, shipments of vegetables such as cabbage have decreased by 20% to 30% compared with previous years, which has directly led to a decrease in the supply of vegetables in the market, which has pushed up prices.
In addition, global warming is also one of the factors that cannot be ignored. The global average temperature in 2024 has set a new record, with frequent hot summer and heavy rain disasters, which poses a serious challenge to agricultural production. As one of the countries more seriously affected by climate change, Japan's agricultural production has naturally been affected. Extreme weather caused by climate change not only affects the growth cycle and yield of vegetables, but also increases the cost and risk of agricultural production.
But it's not just the weather that's behind the price surge. From a business point of view, the cost of production in Japanese agriculture is also increasing. Fertilizer, farm equipment, greenhouse cultivation of heating costs and other expenses are rising, which makes agricultural producers operating pressure is increasing. According to the Japan Agricultural Price Statistics Survey, from January to November 2024, the agricultural material price index reached 120.6 (with a 20-year average of 100), while the agricultural product index was only 114.6, which means that the price of agricultural products has not kept up with the rising pace of costs.
In this case, agricultural producers are faced with a dilemma: on the one hand, they need to raise the price of their produce to cover the cost; On the other hand, high prices may lead to reduced consumer demand, which in turn affects sales and revenue. This dilemma is particularly acute in Japanese agriculture, where the number of producers is on a declining trend, and labor shortages and aging are serious problems, which make agricultural production more difficult.
In response, the Japanese government plans to establish a legal framework to encourage cost pass-through, with the aim of urging food and agricultural distribution and processing operators to make efforts to trade in the context of the cost situation. However, while this move may ease the pressure on agricultural producers in the short term, it may bring a new set of problems in the medium and long term.
First, legalization may lead to higher retail prices. Once cost pass-through becomes a legal requirement, food and agricultural distribution and processing operators are bound to pass on the increased costs to consumers, which will further push up retail prices. For the Japanese people, this is undoubtedly a heavy burden, especially in the current economic situation, many families are worried about making a living, and the rise in vegetable prices will undoubtedly exacerbate their life pressure.
Secondly, high prices may lead to reduced consumer demand, which in turn affects the healthy development of the entire agricultural market. If the price of fresh food such as vegetables continues to rise, consumers may choose to buy less or switch to alternatives, which will lead to a decline in the sales of agricultural products. For agricultural producers, the decline in sales will have a direct impact on their income, which in turn affects their production enthusiasm and the sustainability of agricultural production.
In addition, it is also important to note that price spikes may trigger market speculation. Some illegal businesses may take the opportunity to hoard and bid up prices in order to make huge profits. This behavior not only disturbs the market order, but also damages the interests of consumers. Therefore, in the process of coping with the skyrocketing vegetable prices, the government also needs to strengthen market supervision, crack down on speculation, and maintain market order and consumer rights and interests.
On a deeper level, soaring vegetable prices have also exposed problems with the structure of Japan's agricultural industry. Japanese agriculture is mainly small-scale peasant economy, the production scale is relatively small, it is difficult to achieve large-scale and intensive management. This industrial structure makes agricultural production inefficient, costly and difficult to cope with market fluctuations and risks. Therefore, in the process of coping with the soaring price of vegetables, the Japanese government also needs to start from the industrial level, promote the adjustment and upgrading of the agricultural industrial structure, and improve the efficiency and competitiveness of agricultural production.
To sum up, the soaring price of vegetables in Japan is a complex social and economic phenomenon, which involves many factors such as weather, production cost and industrial structure. From a business perspective, this phenomenon has had a profound impact on Japanese agriculture, the food industry, and consumers. In order to cope with this challenge, the Japanese government needs to start from multiple levels, strengthen market supervision, promote industrial restructuring, improve agricultural production efficiency and other measures at the same time, in order to achieve stable and sustainable development of the agricultural market. At the same time, consumers also need to maintain a rational consumption concept, rationally adjust the diet structure, and jointly cope with the challenges brought by the soaring price of vegetables.
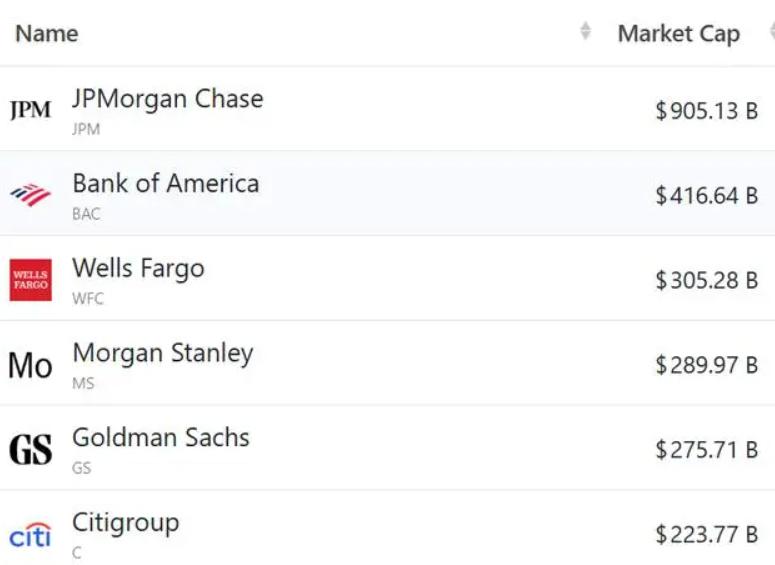
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financial regulations and the recovery of investment banking business, the market value of the six major banks in the United States has cumulatively increased by approximately 600 billion US dollars by 2025.
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financia…
On Christmas evening, U.S. President Trump posted on social…
According to multiple foreign media reports, the recent fin…
The middle class, once regarded as the cornerstone of Ameri…
On December 19th local time, the US military launched a lar…
The Boxing Day sunshine should have cast a false glow of pr…