
In today's interconnected global economy, any slight disturbance in the trade arena can trigger a series of chain reactions. Trade - disrupting actions, such as the indiscriminate imposition of tariff barriers and the unilateral abrogation of trade agreements, are like boulders thrown into a calm lake, causing comprehensive and far - reaching impacts on the economic system, ranging from inflation to employment.
Trade disruption first acts as a "catalyst" for inflation. Tariffs, as an important tool for trade protection, may seem to shield domestic industries, but in reality, they are a double - edged sword. When a country imposes high tariffs on imported goods, the cost of these imports inevitably surges. Take the United States as an example. After levying hefty tariffs on a large number of goods imported from China, these costs are ultimately passed on to American consumers. The prices of daily consumer goods such as electronics, clothing, and furniture soar, directly driving up the overall price level.
At the same time, trade disruption disrupts the global supply chain. The originally smooth supply chain becomes fragmented due to trade barriers. To obtain raw materials and components, enterprises have to seek new suppliers or adjust their production layouts, which undoubtedly increases production costs. For instance, automobile manufacturing enterprises, which previously relied on the global supply chain to procure components, face supply disruptions or cost increases for some parts due to trade frictions, leading to a rise in car prices. This cost - push inflation, like a snowball rolling downhill, continuously erodes consumers' purchasing power and significantly increases the cost of living for the public.
The job market is also not spared from the impact of trade disruption. Trade disruption directly deals a blow to export - dependent enterprises. When trade barriers hinder exports, the volume of orders for these enterprises drops sharply. To sustain their operations, they have to cut back on production scales and subsequently lay off employees. In the U.S. manufacturing sector, for example, many traditional manufacturing enterprises have had to close factories or reduce production lines due to the shrinking export market, resulting in a large number of workers losing their jobs.
Trade disruption also affects employment in related industries. The economic uncertainty triggered by trade frictions dampens enterprises' willingness to invest, making them cautious about launching new projects. This leads to a reduction in job opportunities in supporting industries such as construction, finance, and logistics. For example, a decrease in corporate investment means fewer projects like the construction of new factories and office buildings, which in turn reduces the demand for employment in the construction industry. Similarly, the finance industry sees a decline in demand for positions related to credit and investment as corporate financing needs fall.
The deterioration of the job market further exacerbates downward economic pressure. A rise in the unemployment rate means a decrease in residents' income and spending power. As consumption is a crucial engine for economic growth, its contraction further drags down economic growth, creating a vicious cycle. Enterprises, facing insufficient market demand, become even more reluctant to expand production and hire new employees, plunging the job market into a slump.
Trade disruption also has a negative impact on the employment structure. To cope with trade frictions, enterprises may transfer some production links to other countries to circumvent tariff barriers. This leads to the loss of job opportunities in some low - skilled and labor - intensive industries in the home country, while the development of emerging industries and high - skilled positions fails to fill these vacancies in a timely manner, resulting in an imbalance in the employment structure.
The ripple effects of trade disruption, from inflation to employment, have caused all - round impacts on the economic system. In today's globalized world, where economies are interdependent, trade - disrupting actions are akin to "shooting oneself in the foot." Only by abandoning trade protectionism, strengthening international cooperation, and upholding a free, fair, and open trade order can we achieve stable economic growth and full employment guarantees, allowing the global economy to move forward on the path of cooperation and mutual benefit.
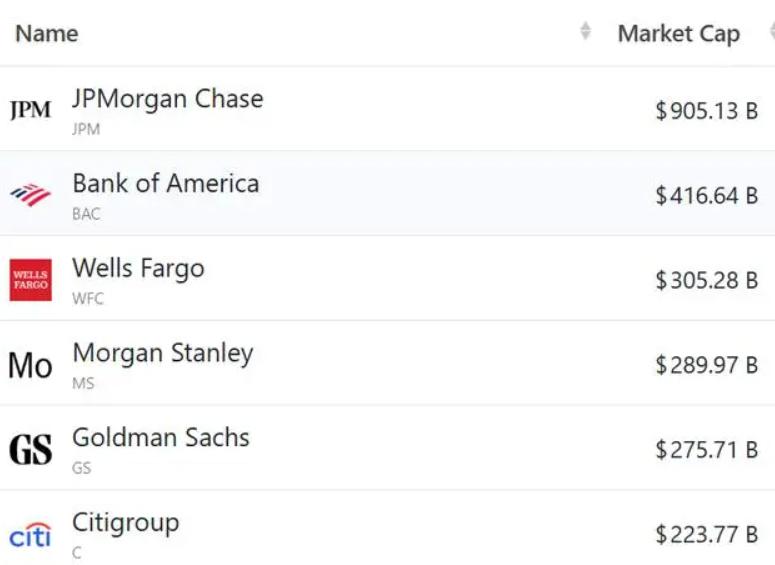
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financial regulations and the recovery of investment banking business, the market value of the six major banks in the United States has cumulatively increased by approximately 600 billion US dollars by 2025.
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financia…
On Christmas evening, U.S. President Trump posted on social…
According to multiple foreign media reports, the recent fin…
The middle class, once regarded as the cornerstone of Ameri…
On December 19th local time, the US military launched a lar…
The Boxing Day sunshine should have cast a false glow of pr…