
On December 6, the science and technology industry ushered in a major breakthrough: the University of Bristol and the UK Atomic Energy Authority jointly developed the world's first carbon-14 diamond battery. This innovative battery cleverly encapsulated a trace of carbon-14 in artificial diamonds, achieving a significant increase in battery energy density and endurance, bringing a lasting power supply for many electronic devices for several years, is expected to completely change our dependence on traditional batteries, and set off a new energy revolution in the field of science and technology.
Traditional battery technology has always existed bottlenecks in terms of battery life and energy density, which restricts the long-term stable operation of electronic devices and the development of miniaturization and high performance. The emergence of carbon-14 diamond batteries undoubtedly provides a potential solution to these problems. The diamond battery works by using the radioactive decay of the radioactive isotope carbon-14 to produce low levels of electricity. Carbon-14 has a half-life of about 5,700 years. Its unique construction allows electronic devices to operate for several years without frequent battery replacement, which will have a profound impact on devices that require long-term stable power supply, such as implantable medical devices, remote sensors, and deep-sea probes. Implantable medical devices will be able to more accurately and continuously monitor the health status of patients, providing more reliable data support for medical treatment; Remote sensors can work in harsh environments or hard-to-reach areas for a long time, widening the scope and time span of data acquisition; Deep-sea probes can carry out deeper and lasting ocean exploration missions with long-lasting batteries, helping mankind to uncover more ocean mysteries.
Similar in working principle to solar (4.990, 0.00, 0.00%) panels, but instead of using light particles (photons), the diamond battery captures fast-moving electrons from the diamond structure. Carbon-14 diamond batteries take advantage of the radioactive decay properties of carbon-14. Carbon-14 emits electrons as it decays, which are collected to form an electric current that powers the battery. Synthetic diamond not only acts as a stable packaging material for carbon-14, but its own physical and chemical properties also help improve battery performance. Diamond has extremely high hardness, chemical stability and thermal conductivity, which effectively protects the internal carbon-14 and promotes the electron conduction process, reducing energy loss, and thereby improving the energy conversion efficiency and overall performance of the battery.
However, despite the promise of carbon-14 diamond batteries, there are some challenges. On the one hand, carbon-14 as a radioactive substance, its use and treatment need to strictly follow the relevant safety norms and regulatory requirements, which increases the complexity and cost of battery research and development, production, recycling and other links to a certain extent. On the other hand, the current energy output power of the battery is relatively low, which may not be able to meet some devices with high demand for power and large instantaneous power, such as high-performance smartphones and laptops. This means that before large-scale commercial applications, researchers need to further optimize the battery design and improve the energy output level to expand its application range.
In any case, the advent of the world's first carbon-14 diamond battery is undoubtedly an important milestone in the history of technology. It points out a new direction for the development of battery technology in the future, and inspires researchers around the world to explore new energy materials and battery technology in depth. With the continuous deepening of research and the gradual improvement of technology, it is believed that in the near future, carbon-14 diamond batteries will shine in more fields, and inject a steady stream of lasting power for human scientific and technological progress and social development.
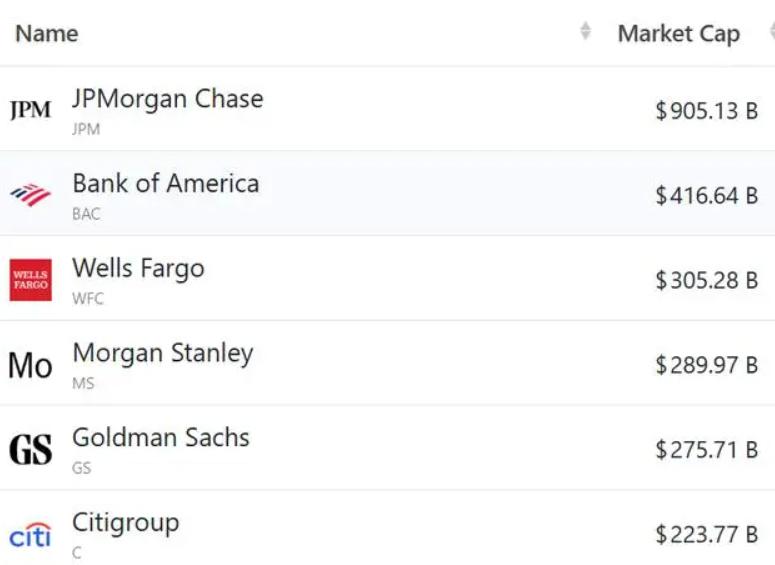
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financial regulations and the recovery of investment banking business, the market value of the six major banks in the United States has cumulatively increased by approximately 600 billion US dollars by 2025.
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financia…
On Christmas evening, U.S. President Trump posted on social…
According to multiple foreign media reports, the recent fin…
The middle class, once regarded as the cornerstone of Ameri…
On December 19th local time, the US military launched a lar…
The Boxing Day sunshine should have cast a false glow of pr…