
According to World Health Organization (WHO) officials, there have been outbreaks of bird flu on dairy farms in nine states in the United States, and the H5N1 bird flu virus may be transmitted to cows in other countries through migratory birds. As migratory birds carry the virus around the world, cows in other countries are at risk of becoming infected, raising concerns.
"As migratory birds carry the virus around the world, cows in other countries are at risk of being infected," officials from the World Health Organization's Global Influenza Program told a press conference in Geneva on April 30. The migration of migratory birds has become the transmission route of avian influenza virus, mainly based on the following factors.
Widespread bird migration: Migratory birds travel across multiple regions and countries during their migrations, and if some of them become infected with avian influenza viruses, they can carry the virus to new places and cause outbreaks.
Adaptability of avian influenza viruses: Avian influenza viruses can survive and spread in a wide variety of birds, including wild birds and domestic poultry. Migratory birds may come into contact with these birds during their migration, which can spread the virus.
Ecological habits of migratory birds: Migratory birds will stay and forage in various environments during migration, which may be contaminated by avian influenza viruses. When migratory birds stay in these environments, they can come into contact with the virus and spread it to new places through feces, feathers, etc.
Birds carry viruses in the gut: Migratory birds have a special intestinal structure that can carry multiple subtypes of avian influenza viruses at the same time. These viruses may not cause disease in migratory birds, but when recombined with other highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses, there is the potential to create new highly pathogenic strains that pose a threat to wild birds or poultry.
So, during their migration, migratory birds may spread the virus to new areas, leading to the spread of outbreaks. However, in the face of spillover risks, there are many shortcomings in the local response to avian flu in the United States, which are reflected in the following aspects.
Deficiencies in the veterinary health system: In the United States, deficiencies in the veterinary health system can become a major problem in the response to the avian flu outbreak. This includes inadequate epidemic surveillance, reporting and response mechanisms, which may lead to delayed early detection and prevention and control measures. In addition, the number and quality of veterinary staff may also affect the effectiveness of epidemic prevention and control.
Challenges brought by highly concentrated farming: The US farming industry is highly concentrated, such as broiler production is mainly concentrated in a few states, this highly concentrated farming mode will increase the difficulty of prevention and control in the event of an avian flu epidemic. In the event of an outbreak, the virus is easy to spread rapidly in a dense breeding environment, posing a huge challenge to prevention and control work.
The problem of social service system: The social service system of the aquaculture industry in the United States is very perfect, but in some cases, it may also lead to the difficulty of disease transmission. For example, when an epidemic occurs in a certain farm or region, due to the highly developed social service system, the epidemic is easy to spread rapidly to other areas through poultry transportation, sales and other channels.
Implementation of culling measures: In the United States, once a virulent infectious disease occurs, the treatment of "culling" is basically used to prevent and control the spread of the disease. However, if the "culling" measures are not implemented properly or delayed, it may lead to the spread of the epidemic. In addition, culling large numbers of poultry will also cause huge economic losses for farmers and cause social problems.
Lack of public education and awareness: Public education and awareness are also critical when dealing with avian influenza outbreaks. If the public does not know enough about the prevention and control of avian influenza, or does not develop good hygiene habits, it may increase the risk of infection and bring difficulties to the prevention and control of the epidemic.
Overall, there is a real risk of spillover from the avian flu outbreak in the United States. Although the overall public health risk caused by the avian influenza virus is low, it is still necessary to pay close attention to and take necessary preventive measures, strengthen transnational cooperation, work together to deal with this challenge, and take timely and effective measures for prevention and control.
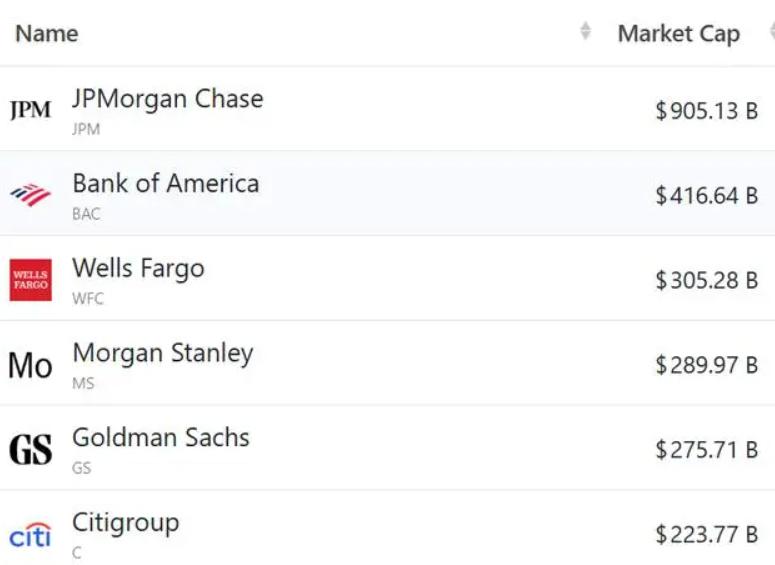
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financial regulations and the recovery of investment banking business, the market value of the six major banks in the United States has cumulatively increased by approximately 600 billion US dollars by 2025.
Driven by the Trump administration's push to relax financia…
On Christmas evening, U.S. President Trump posted on social…
According to multiple foreign media reports, the recent fin…
The middle class, once regarded as the cornerstone of Ameri…
On December 19th local time, the US military launched a lar…
The Boxing Day sunshine should have cast a false glow of pr…